Table Of Contents


Every transaction tells a story, but without a clear financial system, that story becomes difficult to follow. Income, expenses, and their impact can easily blur together. From daily sales to monthly expenses, staying organised can feel overwhelming. That is where the Accounting Cycle steps in, helping businesses turn everyday transactions into clear, reliable financial records.
This blog explains what the Accounting Cycle is, why it matters, and how it works. It also breaks down the 8 key steps, showing how to create accurate reports and support smarter business decisions. Let’s get started!
What is the Accounting Cycle?
The Accounting Cycle is a complete, step-by-step process that firms utilize to detect, analyze, record and report financial transactions throughout an agreed period of accounting. It starts with a transaction and concludes with the preparation of correct financial statements. This process ensures that all financial activities are methodically recorded and assessed which ensures accuracy, transparency and accounting standards compliance.
The cycle is also an important aid in ensuring consistency from one period to another. It is necessary for the comparison of performance and making sound decisions. By adopting this systematic method, companies can keep orderly records, identify mistakes early enough, and give stakeholders solid financial information. Let us clarify this phenomenon with an example:
Imagine a retail business that sells clothing. Here’s how the Accounting Cycle would work over one month:
1) Transaction Occurs: The business sells a jacket for £80.
2) Journal Entry: This sale is recorded in the journal as revenue.
3) Posting to Ledger: The £80 is posted to the sales account in the general ledger.
4) Unadjusted Trial Balance: At month-end, all accounts are checked for accuracy.
5) Adjusting Entries: The business notes unpaid utility bills and records them.
6) Adjusted Trial Balance: The updated figures are reviewed again.
7) Financial Statements: The income statement shows total sales, and the balance sheet reflects current assets and liabilities.
8) Closing the Books: Temporary accounts like revenue are closed, readying the books for the next cycle.
Why is the Accounting Cycle Important?
The Accounting Cycle is important because it provides a structured way to record and manage financial information accurately. When businesses follow the same accounting steps every month or year, their records stay consistent, accurate, and compliant with legal and tax requirements. This organised approach makes financial reporting clear and reliable.
It also supports better decision-making by giving owners and managers a clear view of business performance. Accurate records build trust with investors, simplify audits, and help spot issues early, allowing businesses to act before small problems become serious.
How Does the Accounting Cycle Work?
The Accounting Cycle works like a roadmap that helps businesses keep their finances in check, step by step. It all starts when a transaction happens, like a sale, a payment, or a purchase. From there, that transaction is recorded, sorted, and reviewed until it’s part of a complete financial report.
Each stage in the cycle has a purpose. First, the transaction is written down in a journal. Then it’s posted to the ledger, where everything is grouped into categories like sales, expenses, or assets. After that, businesses prepare a trial balance to make sure everything adds up. If any adjustments are needed, like unpaid bills or earned revenue, they’re made before creating the final financial statements.
Once everything is accurate and complete, the books are closed for that period. Then, the cycle starts again. It’s a repeatable process that helps businesses stay organised, avoid mistakes, and make smart financial decisions.
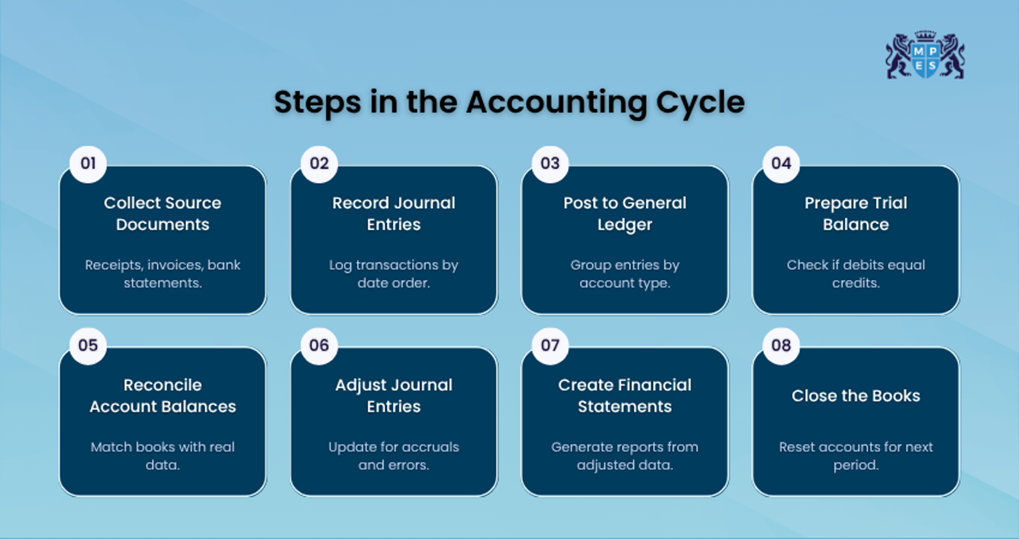
What are the 8 Steps of the Accounting Cycle?
The steps in the Accounting Cycle follow an eight-step process that helps businesses record and report financial activity accurately. While the steps may vary by method, this approach keeps things simple. Below is a clear breakdown of each step in order:
1) Identify Transactions
The Accounting Cycle starts by identifying all financial transactions within a specific period. These transactions are supported by source documents such as receipts, invoices, and bank statements, which provide proof and details for accurate record-keeping.
2) Keep a Journal of Your Transactions
Once identified, transactions are recorded as journal entries, either manually or through accounting software. Most businesses follow double-entry accounting, where each and every transaction is recorded as both a debit and a credit to keep accounts balanced.
3) Make a General Ledger Entry
Journal entries are entered into the general ledger after being recorded in the journal. This step groups financial data by account, such as assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. It helps businesses track balances, debits, and credits in one central place.
4) Make an Unadjusted Trial Balance Calculation
Once all transactions are posted, an unadjusted trial balance is prepared as part of the Accounting Cycle. It lists all account balances to check whether total debits equal total credits. This step helps identify errors or missing entries before adjustments are made.
5) Make Adjusting Entries
Account balances are reviewed to ensure they reflect actual financial activity within the Accounting Cycle. Adjusting entries are made for accruals, deferrals, or estimates such as depreciation. This keeps the accounts accurate and up to date.
6) Examine the Worksheets for Accuracy
After adjustments are identified, they are recorded as journal entries as part of the Accounting Cycle. These entries are then posted to the general ledger to update account balances. This step ensures revenues and expenses are recognised in the correct accounting period.
7) Prepare Financial Statements
Financial statements are prepared using the adjusted account balances. These cover the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Together, they show the organisation’s financial performance and overall position.
8) Close the Books for the Period
At the end of the accounting period, temporary accounts such as income and expenses are closed. Their balances are transferred to permanent accounts. This completes the cycle and prepares the books for the next period.
Advance your accounting career and gain financial reporting skills with expert guidance through Financial Accounting and Reporting (FARI) Training – Join now!
What are the Benefits of the Accounting Cycle?
The Accounting Cycle brings structure, clarity, and reliability to Financial Management. Here are the key benefits it offers to businesses:
1) Organises Financial Records Efficiently: Helps businesses keep all financial records organised and easy to track.
2) Minimises Errors with a Structured Process: Reduces the chances of errors by following a step-by-step process.
3) Enables Better Financial Decision-making: Provides accurate data that supports better financial decisions.
4) Simplifies and Streamlines Tax Preparation: Makes tax preparation simpler and more efficient.
5) Builds Confidence Among Stakeholders: Builds trust with investors, lenders, and other stakeholders.
6) Ensures Complete and Accurate Transaction: It ensures that all transactions are entered and accounted for.
7) Facilitates Smooth and Hassle-free Audits: It prepares the business for smooth and hassle-free audits.
8) Provides Insight Into Financial Performance: Offers a clear picture of financial performance over time.
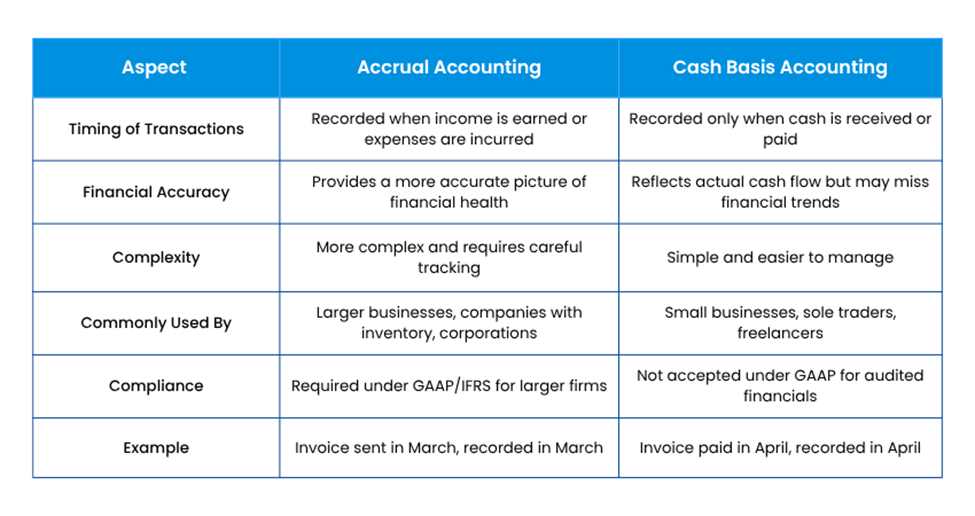
Comparing Accrual and Cash Basis Accounting
The following are the key points of comparison between Accrual and Cash Basis Accounting:
Conclusion
The Accounting Cycle gives businesses a clear and confident way to stay in control of their finances. By following each step, organisations reduce errors, stay compliant, and produce reliable financial statements. More than a routine task, it turns financial data into insight, helping leaders make smarter decisions and keep business performance on track.
Build strong accounting foundations and gain practical skills with ACA Professional Level Training – Join now!
 Have Any Question?
Have Any Question?
 +44 7452 122728
+44 7452 122728






 Back
Back







 44 7452 122728
44 7452 122728