Table Of Contents

Keeping financial records without Account Reconciliation is like guessing your bank balance and hoping it is right. Mistakes build up, surprises appear and stress follows. Reconciliation gives you clarity and control by making sure every pound is tracked and every payment is recorded. When your numbers are accurate, decisions become easier, growth feels smoother, and money worries stay away.
This blog helps you understand why Account Reconciliation matters, how it works and the different types involved. With regular reconciliation, you can keep your finances accurate and enjoy peace of mind knowing your accounts are always correct.
What is Account Reconciliation?
Account Reconciliation is the process of checking if a company’s financial records match documents from outside sources, such as bank statements, invoices, or credit card bills. It helps confirm whether each recorded transaction is accurate and properly documented. This process is also used during audits to verify the reliability of financial statements and improve transparency.
Key Takeaways:
a) Account Reconciliation helps find mistakes and reduce fraud risk
b) It compares internal records with bank statements or invoices to spot differences
c) It keeps financial records accurate and supports good financial health
d) It ensures businesses follow accounting rules and avoid penalties
e) It strengthens credibility with investors, suppliers and stakeholders
d) It helps maintain a clear view of real cash available for smart decisions
Importance of Account Reconciliation
Account Reconciliation is important because it keeps financial records accurate and reliable. By matching internal books with statements like bank records or invoices, businesses can spot errors, prevent fraud, and stay compliant with rules. It also helps them understand their true financial position and make better decisions.
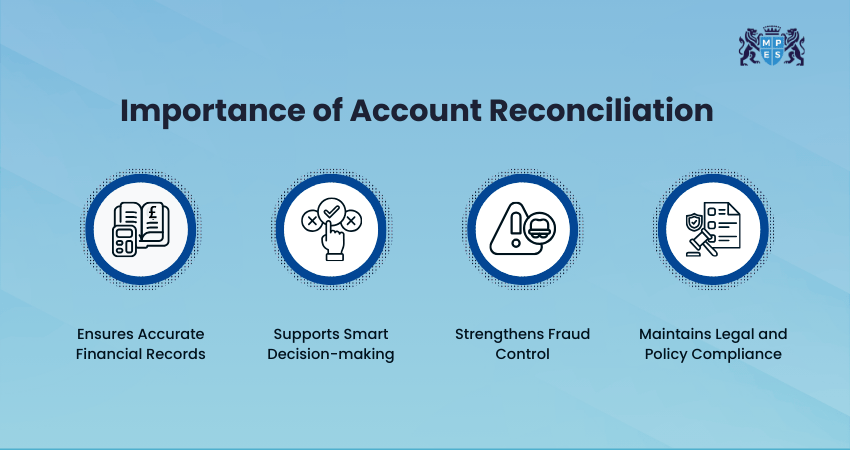
Regular Reconciliation also builds trust among investors, banks, and auditors by showing that financial records are correct and well-maintained. It supports better budgeting, cash flow control, and reduces the risk of unexpected losses. Overall, it helps businesses stay organised, financially stable, and prepared for growth.
How Account Reconciliation Works?
Account Reconciliation compares internal financial records with external documents to ensure all transactions match and errors are found early. It also helps prevent fraud and keeps financial reports reliable. Now, let’s see the simple steps involved in this process.
1) Collect all Relevant Records: Gather internal documents such as ledgers, invoices, journal entries, and receipts. Also, collect external documents, including bank statements or credit card statements, for the same period.
2) Verify Opening Balances: Ensure that the opening balance in your accounting system matches the opening balance on the statement.
3) Match Individual Transactions: Compare each entry recorded in your books with the corresponding transaction on the statement.
4) Identify Differences or Missing Items: Look for unrecorded transactions, duplicate postings, timing delays, or incorrect amounts.
5) Make Necessary Adjustments: Update your financial records by adding missing entries, correcting dates or amounts, and removing duplicates.
6) Validate the Closing Balance: After corrections, check whether the closing balance in your system matches the closing balance on the statement.
7) Maintain Proper Documentation: Store reconciliation reports securely and ensure they are approved or reviewed. They support audits and future Financial Analysis.
Gain confidence in Financial Analysis and compliance with Financial Reporting (FR) Training – Join now!
Types of Account Reconciliation
Different accounts require different reconciliation techniques. Here are the most common types of Account Reconciliation:
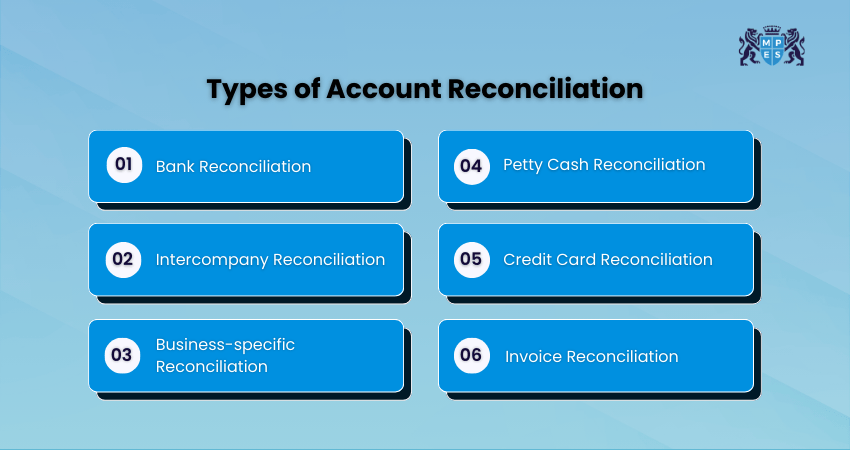
1) Bank Reconciliation
Bank Reconciliation compares the company’s cash records with the bank statement to ensure that deposits, withdrawals, bank fees, interest charges, and pending transactions are accurately recorded. Any differences, such as uncleared cheques or missing charges, are investigated and corrected to show the true cash balance.
2) Intercompany Reconciliation
Intercompany Reconciliation ensures that transactions between subsidiaries, branches, or related entities match accurately. If one unit records an amount sent, the receiving unit must record the identical amount received. This keeps consolidated group-level financial statements reliable.
3) Business-specific Reconciliation
Some reconciliations focus on accounts that are unique to a company’s operations. For example, retailers may reconcile daily sales and returns, while manufacturers may reconcile raw material usage. This helps maintain accuracy in key business processes.
4) Petty Cash Reconciliation
Petty Cash Reconciliation checks small daily expenses such as office supplies or transport. It confirms that every spending has a receipt and is properly recorded, so the remaining cash matches the expected amount, preventing loss or misuse.
5) Credit Card Reconciliation
Credit Card Reconciliation checks the company’s credit card statement against recorded expenses. It ensures that all charges are valid, correctly entered, and not duplicated, helping control spending and detect any unusual transactions.
6) Invoice Reconciliation
Invoice Reconciliation validates invoices against purchase orders, goods delivery slips, and payments released. It ensures the billed amount is accurate and that goods or services were delivered as agreed, reducing disputes and financial discrepancies.
The Account Reconciliation Process
The Account Reconciliation process ensures financial records are accurate by comparing them with external documents and correcting any differences. It helps prevent errors and keeps accounts updated. Here are the main steps involved in Account Reconciliation:
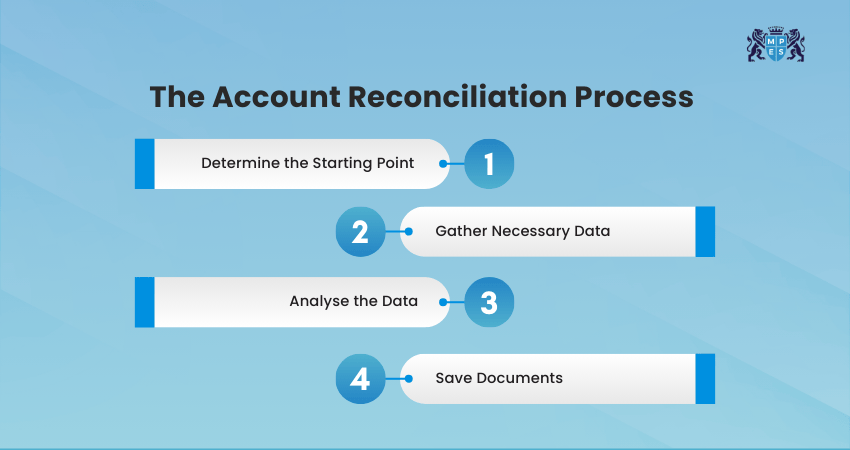
Step 1: Determine the Starting Point
Begin by checking the opening balance of the Account you want to reconcile. This balance should match the closing balance from the previous period. If there is already a difference at the start, note it so you can fix it during Account Reconciliation.
Step 2: Gather Necessary Data
Collect all documents related to the Account for the period you are checking. These may include ledgers, receipts, bank statements, credit card bills or supplier statements. Having complete and correct documents makes reconciliation easier and more accurate.
Step 3: Analyse the Data
Compare each transaction in your records with the information shown in the external documents. Look for any differences such as missing entries, wrong amounts or extra charges. Once you find an issue, adjust your records so the numbers match correctly.
Step 4: Save Documents
After Account Reconciliation is complete, store all supporting files neatly and safely. These documents act as proof that the Account was checked properly. They are useful during audits and when reviewing financial records in the future.
Step 5: Confirm Final Balances Match
After corrections, verify that the ending balance in your financial records matches the ending balance on the external statement. This confirms successful reconciliation.
Strengthen your Financial Analysis and strategy skills with Financial Management (FM) Training - Join now!
How to Perform Account Reconciliation?
Account Reconciliation helps check that the money recorded in your books matches what appears on bank statements or receipts. When both records match, your finances are accurate and safe. Here are the three basic steps:
1) Compare Your Records with Your Bank Statement
Check every transaction in your internal records against the bank statement. Make sure the same amounts appear in both places and keep proof like receipts for confirmation. This helps confirm that all payments and deposits are correctly recorded.
Example: If your records show £50 spent on groceries, the bank statement should also show a £50 deduction.
2) Identify any Discrepancies
Look for differences such as missing entries, duplicate charges, or wrong amounts. Correct these by updating your records. If you think the bank made an error, contact them to confirm. This step ensures that no incorrect or suspicious transaction goes unnoticed.
Example: If your ledger shows a payment of £120 but the bank statement shows £150, you must correct your records to the correct amount.
3) Balance the Records
Once all corrections are made, both records should show the same final balance. This means the Account is successfully reconciled. A matched balance confirms that all transactions have been checked carefully.
Example: If your cash book and your bank statement both show an ending balance of £2,000, the Account is fully reconciled.
Upgrade your professional profile with Performance Management (PM) Training and unlock new opportunities.
Benefits of Account Reconciliation
Account Reconciliation ensures that financial records remain accurate and up to date. Now we’ll look at the key benefits of carrying out this process:
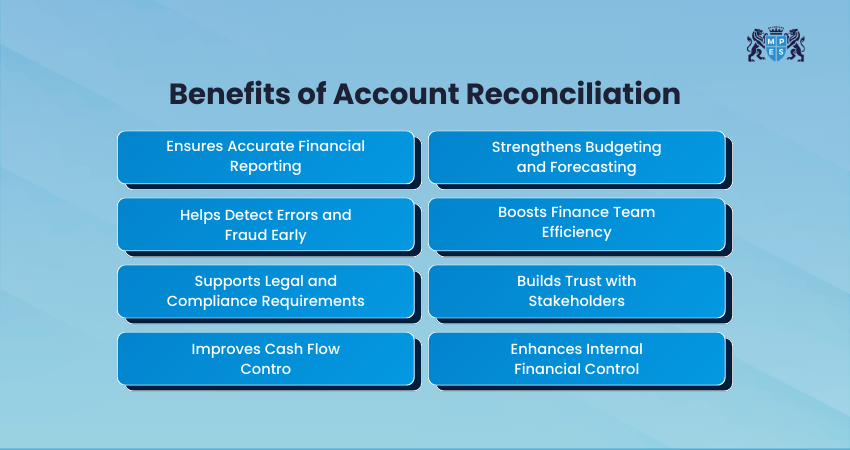
1) Ensures Accurate Financial Reporting: Account Reconciliation keeps financial records correct and trustworthy, helping businesses clearly understand their true financial position and make smart decisions.
2) Helps Detect Errors and Fraud Early: By reviewing accounts regularly, businesses can quickly spot unusual activities or mistakes and correct them before they cause major problems.
3) Supports Legal and Compliance Requirements: Accurate reconciliation helps meet reporting regulations, satisfy audit requirements, and avoid penalties arising from inaccurate records.
4) Improves Cash Flow Control: Reconciliation confirms that every receipt and payment has been recorded, helping companies maintain clear visibility of available cash and manage operating expenses smoothly.
5) Strengthens Budgeting and Forecasting: With precise and updated financial data, organisations can prepare realistic budgets, track spending against plan, and forecast future performance more accurately.
6) Boosts Finance Team Efficiency: Reconciling accounts regularly reduces manual work, speeds up month-end closing, and allows the team to focus on more important financial tasks.
7) Builds Trust with Stakeholders: Accurate records enhance confidence among investors, lenders, management teams, and business partners, supporting financial credibility and long-term relationships.
8) Enhances Internal Financial Control: Account Reconciliation acts as a safety measure, ensuring that every transaction is approved, recorded correctly, and aligned with company policies.
Challenges of Account Reconciliation
Account Reconciliation can become challenging due to time, volume of transactions, and errors in records. Now we’ll look at the key challenges involved in this process:
1. Managing Manual Processes: When Account Reconciliation is done by hand, it takes more time and increases the chance of mistakes. This slows down month-end closing and creates extra pressure on the finance team.
2. Handling Large Transaction Volumes: As businesses grow, the number of transactions grows too. Checking each one carefully becomes difficult and can easily lead to delays.
3. Dealing with Mismatched Data: Differences between internal records and external statements are common. Missing entries, incorrect figures, or duplicate transactions require extra investigation to fix.
4. Managing Timing Differences: Some transactions, such as cheque payments or card settlements, take time to appear in bank statements. These delays can cause temporary imbalances that must be monitored.
5. Technology and System Gaps: If different accounting tools and bank systems do not connect well, data can be incomplete or outdated. This affects accuracy and requires more manual checking.
6. Maintaining Compliance and Audit Readiness: Accurate records are important for audits and financial regulations. Any errors or missing documents make compliance more difficult and stressful.
7. Risk of Fraud Going Undetected: Without regular reconciliation, suspicious or unauthorised activities may remain hidden. Weak internal controls increase the risk of financial loss.
Conclusion
Handling finances without Account Reconciliation is like running a business with guesswork. Reconciliation gives you clarity, confidence, and full control over your money. By making it a regular habit, you avoid surprises, catch issues early, and make smarter financial decisions. Keep your records clean, trust your numbers, and watch your financial future stay strong and secure.
Elevate your accounting career by joining ACCA Applied Skills Training today and gain valuable expertise.
Frequently Asked Questions
FaQ's not available
 Have Any Question?
Have Any Question?
 +44 7452 122728
+44 7452 122728






 Back
Back







 44 7452 122728
44 7452 122728





