Table Of Contents


One tradition in business remains unchanged when it comes to money; estimated costs often replace exact figures on expense lists. Traditional costing methods can miss important details, especially in businesses offering multiple products or services. That’s where Activity-Based Costing (ABC) comes in. It provides a more accurate understanding of your costs, helping you manage them more effectively. Read on to discover what ABC is, how it works, and the benefits it brings.
Table of Contents
What is Activity-Based Costing (ABC)?
A Step-by-step Guide to the Activity-Based Costing Process
Benefits of Activity-Based Costing
Limitations of Activity-Based Costing
Example of Activity-Based Costing
Conclusion
What is Activity-Based Costing (ABC)?
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) is a method used to understand the true cost of products or services in a business. Instead of simply dividing costs evenly, it looks at all the individual tasks or activities involved in production or service delivery.
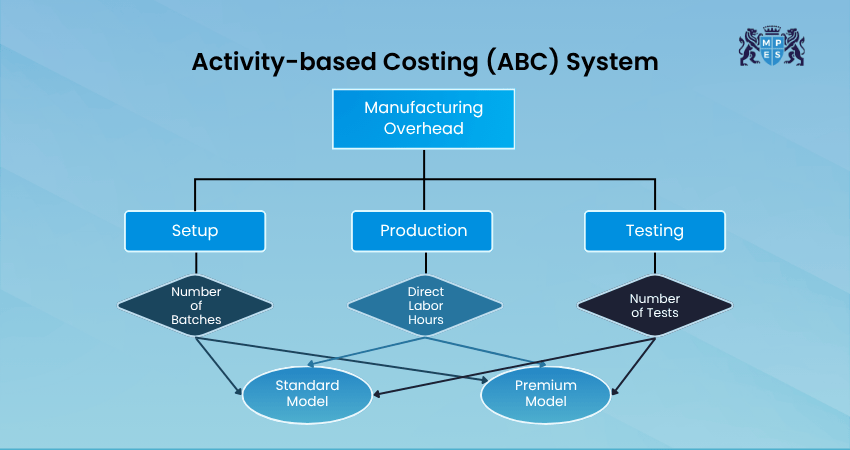
Once these activities are identified, ABC assigns costs based on how much each product or service uses them. This provides a more accurate picture of expenses and helps in smarter decisions around pricing, budgeting, and efficiency.
For example, if you make both chairs and tables, ABC helps you see how much time, effort, and resources go into each one. It is more accurate than simply dividing all the costs evenly.
A Step-by-step Guide to the Activity-Based Costing Process
Activity-Based Costing follows certain steps to achieve accurate pricing for the tasks. Here are the steps involved in the process:
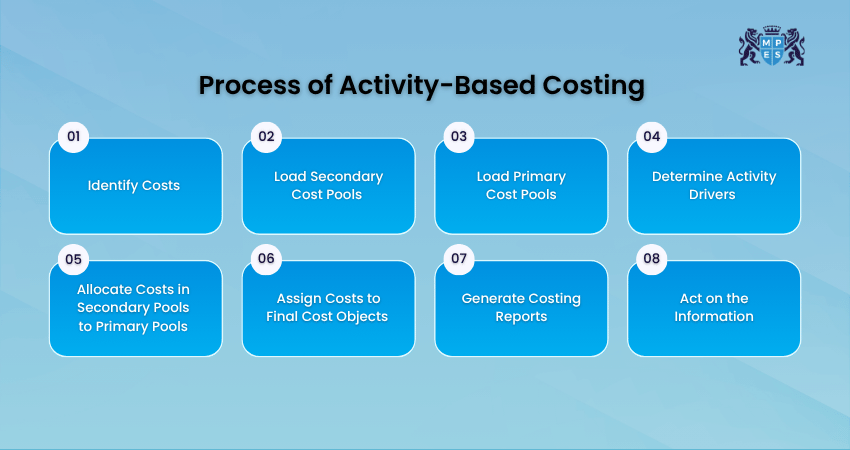
Step 1. Identify Costs
You can start by listing all the costs of your business. These could be direct costs, which are easy to track (like materials), or indirect costs, which are harder to track (like electricity or office rent). This helps you know what you work with. ABC focuses mostly on indirect costs, which are often spread out unfairly in traditional costing.
Step 2. Load Secondary Cost Pools
Some costs support the whole business but don’t directly make products. For instance, IT support teams, HR departments, accounting or office cleaning work. These are added into secondary cost pools to be shared out later. While doing so, these are grouped together so that they can be shared fairly.
Step 3. Load Primary Cost Pools
When you have sorted out the secondary cost pools, now look at the main business activities that actually create your products or services. It includes things like setting up machines, packaging, quality checking, assembling, taking customer orders, and more. Each of these gets its own cost pool.
Step 4: Determine Activity Drivers
Next, you need to figure out what causes each activity to cost money. Activity drivers cause the cost of an activity to go up or down. For example, things like more deliveries, the number of machine setups, or hours spent on design might increase packaging costs. These drivers help track how much each activity is used.
Learn to focus on strategic decision-making and organisational financial health with our Financial Management (FM) Course – Register now!
Step 5. Allocate Costs in Secondary Pools to Primary Pools
The next step in ABC costing is distributing and merging the cost of the pools together. Now, take the supporting costs (from Step 2) and spread them across the main activities. For example, if the IT support team helps both packaging and order processing, its cost is split between those two.
Step 6: Assign Costs to Final Cost Objects
After this, take the costs from each activity and assign them to the actual products or services based on how much they use each activity. This shows the real cost of making each product or offering each service. Knowing these exact costs helps you price your products more accurately and manage profits better.
Step 7: Generate Costing Reports
Use the data you have gathered to make reports. These show you exactly where your money is going and help you understand which products are most costly or most profitable. This might include cost per product or service, cost per customer, profit margins, and more. These reports help Managers make better decisions.
Step 8. Act on the Information
Now that you know how much everything really costs, use that information to make better decisions. Those might involve things like changing prices, cutting waste or altering how things are done. ABC costing is not just about numbers; it is about making smarter choices for your business.
Benefits of Activity-Based Costing
So far, you have been introduced to what ABC costing is and its process. It is time for you to know its benefits. Here are some of its benefits:

1. Adapts to Change
Can be updated quickly when new products or services are added
Adapts well to changes in production methods or business processes
Helps track costs in new departments or product lines
Supports flexible decision-making in dynamic markets
Keeps cost data relevant as processes evolve
2. Improved Workflow
Identifies high-cost activities that need improvement
Reduces waste by highlighting unnecessary tasks
Encourages process improvements across departments
Enhances team coordination by showing activity impact
Makes it easier to streamline operations
3. Future Planning
Provides detailed insights into cost behaviour
Helps create more accurate budgets and forecasts
Assists in evaluating new product or service ideas
Aids in resource planning and capacity management
Supports strategic planning and resource allocation
4. Boosting Long-term Efficiency
Helps eliminate unprofitable products or services
Encourages smarter use of resources over time
Drives continuous improvement in operations
Builds a data-driven culture for long-term success
Strengthens profit margins by improving cost control
Become an expert in financial accounting and reporting by signing up for our Financial Accounting and Reporting (FARI) Course immediately!
Limitations of Activity-Based Costing
While Activity-Based Costing offers many advantages, it also comes with certain challenges. These limitations can affect the accuracy, ease of use, and overall effectiveness of your business. Let's check what are the limitations that come with ABC:
1. High Dependence on Data Accuracy
ABC relies on accurate and updated data.
Errors in data or missing activities can distort cost results
Even small data mistakes can lead to large costing errors
Choosing incorrect cost drivers causes confusion and inaccuracy
Regular data updates are essential to maintain accuracy
2. Limited Insight from One-time Data
ABC based on one-time data does not reflect ongoing business changes
It may miss seasonal trends, sudden shifts, or process changes
Decisions made on outdated data can lead to incorrect pricing
Without regular updates, ABC loses relevance and accuracy
Continuous data collection is needed for long-term effectiveness
3. Complex Data Collection Requirements
Needs inputs from various departments: finance, operations, HR, etc.
Lack of collaboration can slow or disrupt costing
Data from different systems may be hard to combine
May require new tools or integrations to gather complete data
Cross-functional teamwork is critical
4. Inability to Capture Idle Time
ABC mainly tracks active tasks and may miss idle periods
Downtime (e.g., machines waiting or employees idle) is often excluded
Ignoring idle time can hide inefficiencies and inflate productivity data
Total operational costs may be underestimated as a result
Requires separate tracking systems to capture and allocate idle costs
5. Greater Information and System Demands
ABC needs more detailed information than traditional costing methods
Collecting this data takes time, tools, and trained staff
Adds to the workload of finance or operations teams
Might require software upgrades or system changes
Employees may need training to manage the process
6. Complexity in Implementation and Use
ABC can be too complex for smaller businesses
It often requires training, special software, or external expertise
Understanding and maintaining the system may take time
High complexity can slow processes and increase workload
For some companies, the effort may outweigh the benefits
Example of Activity-Based Costing
Let’s look at an example to clearly understand how Activity-Based Costing works. Let's say a business makes two products: wooden chairs and wooden tables. Using traditional costing, they might split the overhead costs 50/50. But in reality, chairs take more work and time because of extra shaping and painting.
Due to such conditions, with ABC, you can check things like:
Observing all activities: cutting, assembling, sanding, painting, checking quality
Calculate how much each activity costs
Work out how often each product uses those activities
Assign the costs fairly based on usage
With this screening, they found that chairs actually use 60% of the activities and tables only 40%. This helps the business see that chairs cost more to make, so they may need to be priced higher, or the production process improved.
Conclusion
Activity-Based Costing helps businesses understand the true cost of making products or providing services. Yes, it takes more time and effort than traditional costing, but the insights it provides are often worth it, especially for companies with many products or complex operations. If you are looking for a smarter way to manage costs and grow your business, ABC could be a great choice.
Understand organisational structures, technological advancements, and financial frameworks with our Business, Technology & Finance (BTF) Course – Join soon!
 Have Any Question?
Have Any Question?
 +44 7452 122728
+44 7452 122728






 Back
Back







 44 7452 122728
44 7452 122728





