Table Of Contents

You may be making great sales, but if customers do not pay on time, your business can still struggle to survive. Unpaid invoices can quietly drain cash flow, delay daily operations, and force businesses to rely on borrowing. This is where Accounts Receivable becomes mandatory for your business.
When managed well, it supports healthier cash flow and stronger financial control. In this blog, we’ll explore what is Accounts Receivable, why it matters, and how the AR cycle works to support financial stability. Let's get started!
What is Accounts Receivable (AR)?
Accounts Receivable, usually called AR, is the money that customers owe a business for products or services that have already been delivered but not yet paid for. In simple terms, it is unpaid customer bills that are expected to be settled within an agreed credit period.
From an Accounting perspective, Accounts Receivable is recorded as a current asset on the balance sheet. For example, if a customer is given 30 days to make a payment, that amount becomes AR until the payment is received.

Why are Accounts Receivables Important?
Accounts Receivable are important because they directly affect how much cash a business has to run day-to-day operations. Cash is needed to pay employees, suppliers, rent, taxes, and other expenses. If money is stuck in unpaid invoices, the business may need to borrow funds or delay payments to others.
Accounts Receivable also shows how well a company manages customer payments. If receivables keep increasing, it may mean that customers are not paying on time. This can be a warning sign of weak credit control or financial trouble among customers. So, to maintain proper financial health, AR must be managed and monitored carefully.
The Accounts Receivable Process Cycle Explained
The Accounts Receivable process cycle is the full journey from the moment a customer places an order until the business receives and records the payment. Each step in this cycle plays a role in making sure payments arrive on time. Let's check the process involved in AR:
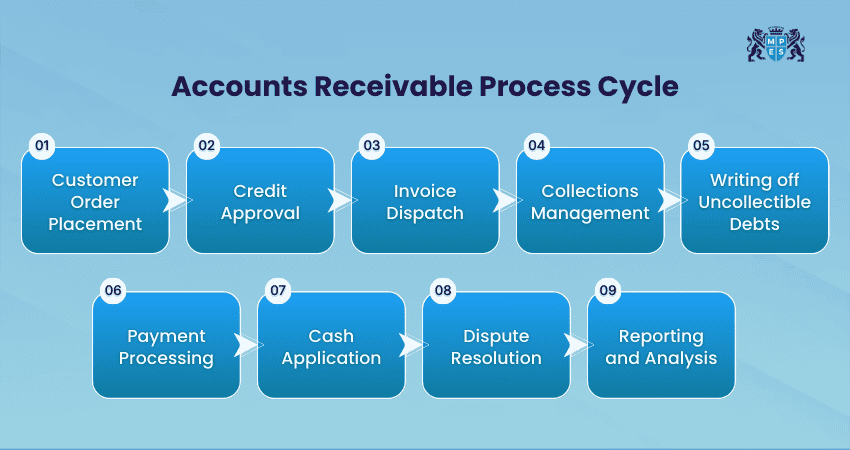
Step 1: Customer Order Placement
The Accounts Receivable process starts when a customer places an order for goods or services. At this stage, the business agrees with the customer on pricing, quantity, delivery details, and payment terms. Clear order details help prevent confusion and payment issues later.
Step 2: Credit Approval
Before allowing a customer to pay later, the business checks whether the customer is reliable. This involves reviewing past payment behaviour, credit history, or financial strength. Credit approval helps reduce the risk of late payments and unpaid invoices.
Step 3: Invoice Dispatch
After delivering the goods or completing the service, the business sends an invoice to the customer. The invoice includes details such as invoice number, amount due, payment deadline, and payment instructions. Sending clear and accurate invoices on time helps customers pay without delay.
Step 4: Collections Management
This step focuses on reminding customers to pay their invoices. Businesses may send reminder emails or make follow-up calls before and after the due date. Regular and polite follow-ups help reduce late payments.
Step 5: Writing off Uncollectible Debts
When repeated follow‑ups fail and a customer is unable or unwilling to pay, the business may write off the amount as an uncollectible debt. This ensures the financial records stay accurate and do not overstate assets. Writing off bad debts also helps reflect the true financial health of the company.
Step 6: Payment Processing
When the customer makes a payment, the business receives it through methods like bank transfer, cheque, or online payment. Payment processing ensures that the money is received safely and recorded correctly.
Step 7: Cash Application
Cash application is the process of matching received customer payments to the correct invoices. This step updates customer accounts and shows which invoices have been paid. Accurate matching helps avoid errors and misunderstandings.
Step 8: Dispute Resolution
Suppose a customer has questions or issues with an invoice, such as incorrect charges, the business reviews and resolves the problem. Quick dispute handling helps avoid long payment delays and keeps customers satisfied.
Step 9: Reporting and Analysis
In the final step, the business reviews Accounts Receivable reports. These reports show unpaid invoices and payment trends. Regular analysis helps businesses improve collections, identify risks, and maintain healthy cash flow.
Gain practical knowledge of income tax, corporation tax, and VAT through the Principles of Taxation (PTX) Course – Register today!
What are the Differences Between Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable?
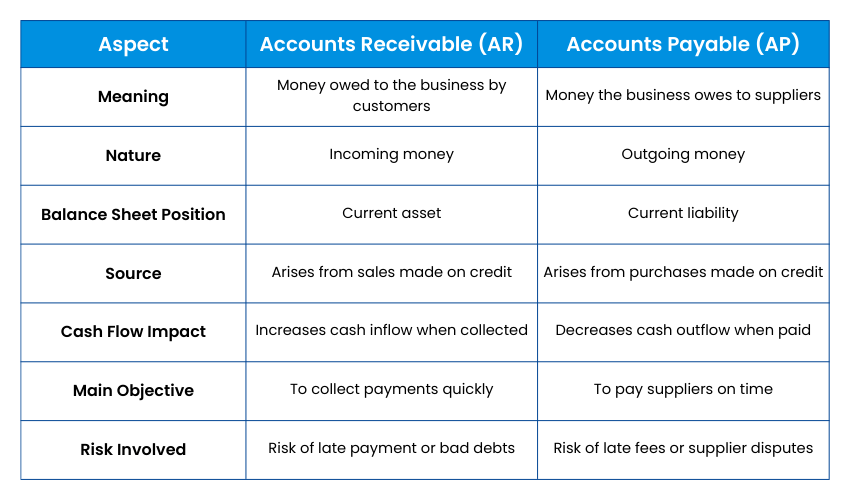
Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable (AP) are often mentioned together, but they represent opposite sides of a company’s financial transactions. While Accounts Receivable refers to money owed to the business by customers, accounts payable represent money the business owes to its suppliers.
AR focuses on collecting money, but AP focuses on making payments. Both need to be managed carefully to keep cash flow balanced. Let's look at their differences with the table below:
What are the Benefits of Accounts Receivable?
Accounts Receivable offers several benefits that help businesses run smoothly and stay financially stable. Understanding these benefits helps businesses see why strong AR practices are essential for long-term success. So, here are its benefits:
1) Improves Cash Flow: Collecting payments on time ensures that the business has enough cash to cover daily expenses and operations.
2) Supports Business Growth: Offering credit makes it easier for customers to buy, which can help increase sales and attract more customers.
3) Strengthens Customer Relationships: Clear payment terms and polite follow-ups create trust and encourage long-term customer relationships.
4) Enhances Financial Planning: Accurate Accounts Receivable records help businesses forecast incoming cash and plan budgets more effectively.
5) Reduces Late Payments and Losses: Regular tracking helps identify overdue invoices early and lowers the risk of unpaid bills.
6) Increases Operational Efficiency: Simple and organised AR processes reduce manual work and make payment tracking easier.
Learn how assurance engagements develop practical audit skills through Assurance (AS) Training – Sign up soon!
Tips to Improve Your Accounts Receivable
Managing Accounts Receivable effectively helps businesses receive payments on time and avoid cash flow issues. The following tips offer simple and practical ways to strengthen your AR process:
1) Set Clear Payment Terms
Clear payment terms help customers understand when payments are due, and this avoids further confusion. When expectations are set early, payments are more likely to arrive on time.
1) Mention due dates clearly on quotes and invoices
2) Set credit limits based on customer history
3) Explain late fees in simple language
4) Keep payment rules consistent across teams
2) Send Invoices Promptly
Sending invoices without delay helps start the payment process quickly. The quicker the invoice is sent, the sooner payment is likely to follow.
1) Avoid holding invoices for monthly billing cycles
2) Use digital invoicing to save time
3) Send invoices during working hours
4) Keep a clear record of sent invoices
3) Ensure Invoice Accuracy
Accurate invoices reduce payment delays caused by questions or corrections. Customers pay faster when invoices are clear and error-free.
1) Check prices and quantities carefully
2) Use the correct customer details
3) Add clear descriptions of goods or services
4) Include valid reference or order numbers
4) Follow up Regularly
Regular follow-ups remind customers about payments without pressure. Friendly reminders help keep invoices from being forgotten.
1) Send reminders before due dates
2) Use email for quick communication
3) Stay polite and professional
4) Track responses to follow-ups
5) Offer Easy Payment Options
Simple payment options make it easier for customers to pay on time. Convenience often leads to faster payments.
1) Accept online and bank payments
2) Provide clear payment instructions
3) Reduce the steps needed to complete the payment
4) Allow customers to choose payment methods
6) Monitor Accounts Regularly
Regular AR checks help businesses spot late payments early. This allows quick action before small issues grow bigger.
1) Review unpaid invoices weekly
2) Group overdue accounts by age
3) Set reminders for overdue payments
4) Update records after every payment
Accounts Receivable Example
Now, let’s check how Accounts Receivable works with an example:
Business Scenario
A furniture manufacturing company sells office chairs worth £8,000 to a corporate customer and offers a 30-day payment term for the invoice.
Invoice Issuance
After delivering the goods, the company raises an invoice for £8,000 and records the amount as Accounts Receivable since payment has not yet been received.
Outstanding Period
During the 30-day credit period, the finance team monitors the unpaid invoice and sends a reminder to the customer before the due date.
Payment Receipt
The customer settles the invoice within the agreed time. Once the payment is received, the amount is cleared from Accounts Receivable and recorded as cash in the company’s accounts.
This example shows how Accounts Receivable represents unpaid invoices during the credit period and how proper follow-ups help businesses collect payments on time and maintain healthy cash flow.
Conclusion
Accounts Receivable is more than just unpaid invoices; it is a key part of a business’s financial health. When the process is managed well, it improves cash flow, reduces payment delays, and helps businesses operate smoothly. By regularly reviewing receivables and following up on payments, businesses can gain better control over their finances and support stable, long-term growth.
Strengthen your Accounting fundamentals with ACA Certificate Level Training – Begin your journey now!
 Have Any Question?
Have Any Question?
 +44 7452 122728
+44 7452 122728






 Back
Back







 44 7452 122728
44 7452 122728




