Table Of Contents


Managing money is one of the toughest challenges for any business, yet many organisations still struggle to see exactly where their costs are coming from. When you cannot track your expenses clearly, profits can quietly slip away. That is where Cost Accounting makes a real difference. It shows how money moves through your business and reveals where value is gained or lost.
Cost Accounting supports smarter pricing, stronger planning, and better decisions by clearly categorising costs and applying effective costing techniques. In this blog, you will discover What is Cost Accounting, explore its types and methods, and understand its key advantages. Let’s get started. ed!
What is Cost Accounting?
Cost Accounting is a type of accounting that focuses on recording, classifying, analysing, and allocating costs associated with producing goods or delivering services. Its primary purpose is to help businesses understand their cost structure and use that insight to improve efficiency and profitability.
Managers use Cost Accounting to plan budgets, control spending, and improve efficiency. It helps determine the cost per unit, identify high-spending departments, and highlight key areas for potential savings.
Types of Costs Used in Cost Accounting
To understand costs clearly, Cost Accounting divides expenses into different categories. Each type of cost provides useful information for planning and control. Those types include the following:
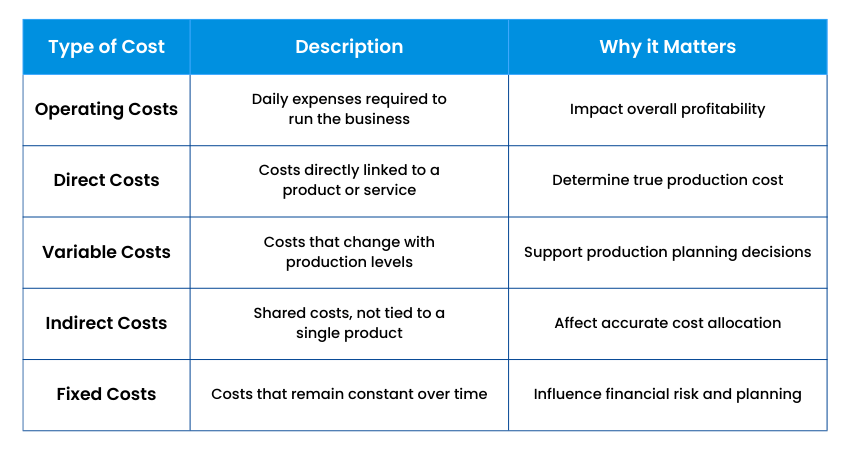
1) Operating Costs
Operating costs are expenses that occur during normal business activities. These costs are required to keep the business running on a daily basis. Examples include materials, salaries, office supplies, maintenance, and marketing costs.
In Cost Accounting, operating costs are closely tracked because they affect overall profitability. Even small savings in operating costs can make a big difference over time.
2) Direct Costs
Direct costs are expenses that can be directly linked to a specific product, service, or project. Common examples include raw materials used in production and wages paid to workers who manufacture goods.
These costs are important in Cost Accounting because they show the true cost of producing something. If direct costs are not measured correctly, a business may set prices too low and lose money.
3) Variable Costs
Variable costs change depending on the level of activity or production. When production increases, these costs increase, and when production decreases, they decrease. Examples include raw materials, packaging, and sales commissions.
Cost Accounting helps businesses understand how variable costs behave. This information is useful for planning production levels and deciding whether to accept extra orders.
4) Indirect Costs
Indirect costs are expenses that support business operations but cannot be linked to a single product or service. Examples include factory rent, utility bills, management salaries, research and development expenses, and equipment depreciation.
Allocating indirect costs correctly is one of the most difficult parts of Cost Accounting. If these costs are shared unfairly, product costs may appear higher or lower than they really are.
5) Fixed Costs
Fixed costs remain the same regardless of how much a business produces, at least within a certain range. Examples include rent, insurance, taxes, and salaries of permanent staff.
Understanding fixed costs helps businesses plan for the future. High fixed costs increase financial risk because they must be paid even when sales are low.
Learn how financial information is recorded and reported through the Financial Accounting (FFA) Course – Register today!
Methods of Cost Accounting
Cost Accounting methods vary across businesses depending on their size, industry, and operational requirements. Below are the most commonly used methods:
1) Marginal Costing
Marginal costing focuses only on variable costs when calculating the cost of a product. Fixed costs are treated as general expenses and are not included in product cost calculations.
This method is helpful for short-term decisions. It helps managers understand how much extra cost is involved in producing one more unit. This is often used for pricing decisions, special orders, and deciding whether to increase production.
Example: A company considers only the additional cost of wood and labour to decide whether accepting a bulk order of 500 extra chairs at a lower price would be profitable.
2) Standard Cost Accounting
Standard Cost Accounting sets expected costs for materials, labour, and overheads before production begins. These standard costs are then compared with actual costs.
When actual costs are higher or lower than expected, the difference is called a variance. Managers analyse these variances to understand what went wrong or what went well. This method helps with cost control and performance measurement.
Example: The company sets a standard cost for wood, labour, and overheads per chair and compares it with actual production costs to identify inefficiencies.
3) Activity-Based Costing (ABC)
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) assigns costs based on activities that use resources. It identifies activities such as machine setup or quality checks and assigns costs based on how much each product uses these activities.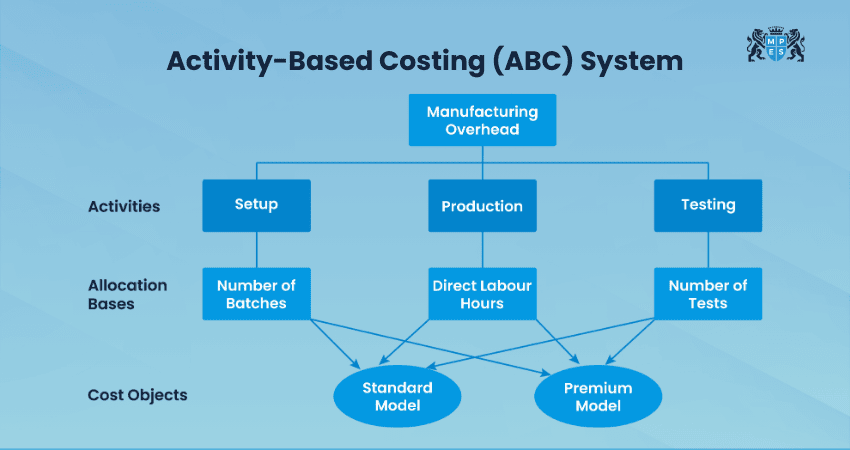
This method provides more accurate cost information, especially for businesses with many products or services. It also helps identify waste and improve efficiency.
Example: Costs such as machine setup, polishing, and quality inspection are assigned to chairs based on how much each activity is used during production.
4) Job Costing
Job costing records costs for individual jobs, projects, or contracts. Each job is treated separately, making it easy to track its total cost and profitability.
This method is common in industries such as construction, consulting, and custom manufacturing. Job costing helps businesses manage budgets and ensure projects remain profitable. It requires careful record-keeping and regular monitoring.
Example: For a custom luxury chair order, all related materials, labour, and overheads are recorded separately to calculate the true cost of the job.
5) Process Costing
Process costing is used when products are made in large quantities and are identical. Costs are collected for each production process and then averaged over all units produced.
This method is suitable for industries such as food processing, chemicals, and textiles. It simplifies cost calculation but does not provide detailed information for individual units or stages.
Example: For mass-produced standard chairs, total monthly production costs are divided by the number of chairs produced to calculate the average cost per chair.
6) Lean Accounting
Lean accounting supports businesses that follow Lean Management practices and value stream mappings. It focuses on reducing waste, improving value, and simplifying financial reporting.
Instead of complex cost allocations, Lean Accounting uses clear and simple reports that managers can easily understand. This method aligns accounting with operational goals but may not meet all traditional accounting requirements.
Example: The company analyses the entire value stream of chair production to remove waste, reduce delays, and focus only on activities that add value to customers.
Support real-world business planning with the Management Accounting (FMA) Course – Join now!
Advantages of Cost Accounting
Cost Accounting offers many advantages that help businesses operate more efficiently and make better decisions. Below are some of the benefits:
1) Improved Cost Monitoring and Control
1) Helps track expenses regularly and systematically
2) Identifies cost overruns at an early stage
3) Highlights wasteful or unnecessary spending
4) Enables better budget control across departments
5) Supports corrective action before losses increase
6) Improves accountability for cost management
7) Ensures resources are used efficiently
2) Enhanced Decision-making
1) Provides accurate cost data for planning decisions
2) Supports pricing and product mix decisions
3) Helps evaluate expansion or investment options
4) Reduces reliance on assumptions and estimates
5) Improves confidence in managerial choices
6) Assists in risk assessment and cost forecasting
7) Aligns decisions with profitability goals
3) Effective Comparison of Business Alternatives
1) Helps compare in-house production vs outsourcing
2) Evaluates cost differences between suppliers
3) Supports make-or-buy decisions
4) Assists in selecting the most profitable product line
5) Compares alternative processes or technologies
6) Improves resource allocation decisions
7) Encourages cost-effective strategic choices
4) Adaptability to Changing Business Needs
1) Adjusts easily to business growth or restructuring
2) Supports costing for new products or services
3) Adapts to changes in production methods
4) Allows updates to costing techniques when needed
5) Works for small, medium, and large organisations
6) Supports continuous improvement initiatives
7) Remains relevant in changing market conditions
Disadvantages of Cost Accounting
Although Cost Accounting is useful, it also has some limitations that businesses should consider. Here are some of the disadvantages of it:
1) May Depend on Highly Skilled Personnel
1) Requires trained and experienced Cost Accounting professionals
2) Risk of errors if staff lack technical knowledge
3) Increases recruitment and training expenses
4) Difficult for small businesses with limited resources
5) Depends heavily on accurate data interpretation
2) May Require Capital Investment
1) Requires spending on accounting software and systems
2) Involves training costs for employees
3) Advanced costing methods increase implementation costs
4) Ongoing maintenance and update expenses
5) May not provide immediate financial returns
3) May Overemphasise Short-term Decisions
1) Focuses mainly on short-term cost reduction
2) May ignore long-term operational efficiency
3) Can lead to reduced investment in employee development
4) Risk of cutting essential quality or maintenance costs
5) Requires careful balance with strategic planning
4) May Lead to Complex Decision-making
1) Involves a large amount of cost data that can be hard to understand
2) Different costing methods may confuse managers
3) Too much information can slow down decision-making
4) Cost reports need to be clear to avoid wrong conclusions
5) Decisions may become difficult if cost data is not linked to business goals
Conclusion
Cost Accounting helps businesses understand their costs and use resources more effectively. By properly analysing What is Cost Accounting, different types of costs and applying suitable costing methods, organisations can improve efficiency and profitability. When aligned with long-term business goals, it becomes a powerful tool for building financial stability and sustainable growth.
Enrich your knowledge of accounting and finance through ACCA Foundations Training - Explore now!
Frequently Asked Questions
FaQ's not available
 Have Any Question?
Have Any Question?
 +44 7452 122728
+44 7452 122728






 Back
Back







 44 7452 122728
44 7452 122728





