Table Of Contents


True digital transformation does not happen through upgrading tools alone. Many organisations invest in modern platforms and automation for instant results. Yet without regularly reviewing and refining your performance, those tools can fail to deliver long-lasting value. Because real transformation needs a structured approach to Continual Service Improvement.
These improvement strategies ensure IT services are measured, analysed, and adjusted to align with changing business goals and deliver consistent results. In this blog, you will discover what is Continual Service Improvement, how it works, and its key processes to attain its true value. Let's dive in!
What is Continual Service Improvement (CSI) in ITIL?
Continual Service Improvement (CSI) is a core component of the ITIL Service Management lifecycle. It focuses on reviewing IT services, processes, and performance metrics to identify areas where improvement can be made. Its primary goal is to enhance service quality, operational efficiency and alignment with business needs using structured methods such as the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle.
Being a part of ITIL improvement philosophy, CSI encourages organisations to adopt a culture of ongoing evaluation and refinement. This is achieved through continuous measurement, analysis, and optimisation of IT services.
ITIL Service Lifecycle
The ITIL service lifecycle is the foundation of the ITIL framework. It provides an organised way to plan, deliver, manage, and improve IT services. The lifecycle covers the entire journey of IT Service Management in five stages. Here are those five stages of ITIL service lifecycle:
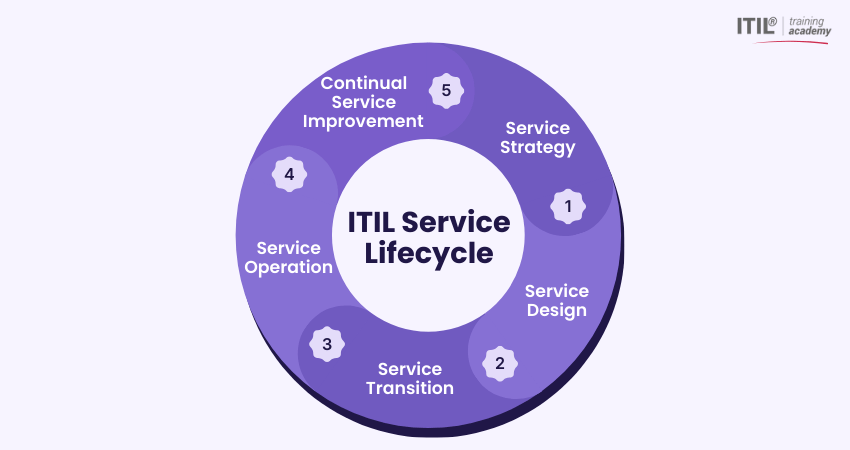
1) Service Strategy: Defines what IT services the business needs and how they will create value.
2) Service Design: Plans and designs services that meet business requirements.
3) Service Transition: Moves new or updated services into the live environment smoothly and safely.
4) Service Operation: Manages and supports IT services on a daily basis to keep them running effectively.
5) Continual Service Improvement: Regularly reviews and improves services at every stage to ensure they align with business goals.
KPIs of Continual Service Improvement
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are central to measuring the success of Continual Service Improvement. It shows how well a service or process is performing. Without KPIs, organisations may implement changes but struggle to prove their effectiveness or identify areas that still require attention.
Below are some important KPIs commonly used in ITIL Continual Service Improvement:
1) Process and Efficiency Metrics
These KPIs evaluate how well internal processes are functioning and improving.
1) First Contact Resolution (FCR) Rate: Shows how many issues are fixed by the first support team without needing to pass them to higher levels.
2) Change Success Rate: Measures how many changes were made without causing service disruptions or rollbacks.
3) Process Compliance Rate: Shows how well teams follow the rules and procedures.
4) Process Efficiency Rate: Measures how smoothly and effectively work is done, reducing waste and delays.
5) Repeated Contact Rate: Tracks how often users report the same issue again, showing if problems were properly resolved.
2) Performance and Reliability Metrics
These KPIs measure your IT service stability, speed, and system reliability.
1) System Availability or Uptime: Shows how often the service is running without interruption.
2) Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF): Measures how long a system runs before it breaks down.
3) Mean Time to Repair (MTTR): Measures the average time taken to restore services after failure.
4) Incident Volume: Tracks how many issues are reported before and after improvement services.
5) Response Time: Measures how quickly systems or services respond to user requests.
3) Service and Quality Metrics
These KPIs focus on customer experience and overall IT service improvement and delivery quality.
1) Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) and Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measure how satisfied users are and how likely they are to recommend your services.
2) Resolution Time & Average Handling Time (AHT): Measure how long it takes to fix an issue or handle a request.
3) Wait Time or Queue Length: Shows how long users wait before getting support from the service desk.
4) Service Reliability and Performance Improvements: Track measurable improvements in availability, response time, and incident reduction following changes.
Ready to improve service stability and governance? Register for ITIL® 4 Specialist: Plan, Implement and Control Training now!
7 Steps in Continual Service Improvement Process
The CSI process provides a clear and structured method for identifying, analysing, and implementing improvements within IT services. Instead of making changes randomly, this step-by-step approach ensures that improvements are based on data, aligned with business goals, and carefully evaluated. Let's check those seven steps involved: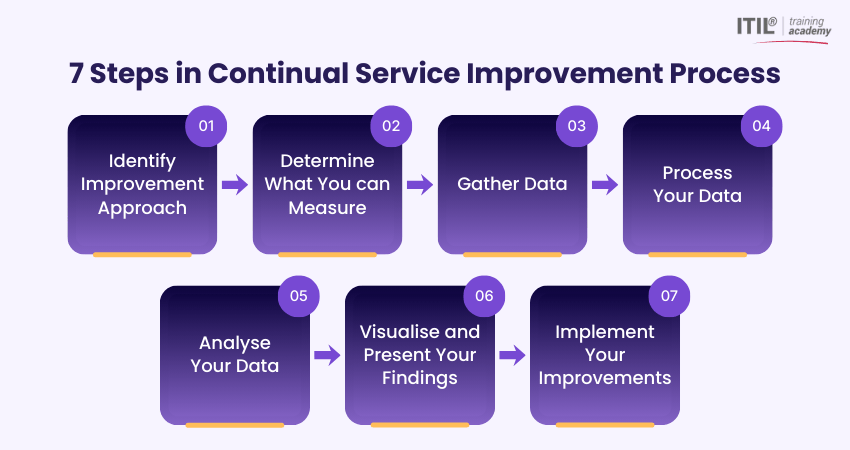
1) Identify Improvement Approach
The first step involves defining the vision and strategy for improvement. It helps determine why improvement is needed and how it supports overall business objectives. This includes reviewing business goals, service strategies, available resources, and identifying areas where service performance needs enhancement.
2) Determine What You can Measure
After identifying what should be measured, the next step is to assess what can realistically be measured. Budget limits, tools, and available data may restrict measurement capabilities. If certain important metrics cannot currently be tracked, this stage is also an opportunity to explore whether resources can be adjusted to enable better measurement.
3) Gather Data
Once measurement areas are confirmed, data collection begins. Monitoring systems generate large amounts of information, and this can include performance reports, customer feedback, incident logs, and system data. The accuracy of data is very important for reliable insights since poor data can lead to wrong decisions.
4) Process Your Data
Raw data often contains gaps, duplicates, or irrelevant information. In this step, the collected data is cleaned, organised, and aligned by sorting, filtering, or summarising them. This ensures that the scattered data gets converted into a useful format for analysis. Proper data processing also improves accuracy and prevents wrong decisions.
5) Analyse Your Data
After processing, the data is analysed to identify trends, patterns, performance gaps, and improvement opportunities. This may reveal recurring incidents, Service Level Agreement (SLA) breaches, or performance bottlenecks. Careful analysis helps organisations understand root causes and make informed decisions about where improvements are truly needed.
6) Visualise and Present Your Findings
The results of your analysis need to be shared with stakeholders such as managers, executives, or clients. Charts, reports, and dashboards help explain the findings clearly. Effective communication ensures everyone understands the key insights and the actions that need to be taken for improvement.
7) Implement Your Improvements
Finally, this step focuses on putting improvements into action. Based on the analysis and feedback, corrective measures are implemented. These may involve process adjustments, system upgrades, staff training, or policy updates. Once implemented, performance is monitored again to measure impact. The cycle then repeats for continuous improvement.
Gain the practical skills needed to manage service assets with ITIL® 4 Practitioner: Service Configuration Management Training – Join now!
Benefits of Implementing ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
Organisations that implement ITIL Continual Service Improvement experience significant operational and strategic benefits. Below are those benefits:
1) Enhanced Service Quality
Continuous monitoring and improvement help reduce errors, minimise service disruptions, and address recurring issues. Over time, services become more stable, reliable, and consistent. This directly improves customer trust, service quality, and overall user experience.
2) Increased Efficiency and Cost Savings
CSI helps identify inefficient processes and eliminate unnecessary steps or waste. By streamlining workflows where possible, organisations can operate more effectively. Though this requires time and resources, the long-term savings and productivity gains outweigh the initial investment.
3) Better Alignment With Business Objectives
Continual Service Improvement ensures that IT services consistently support business priorities. Regular reviews keep services aligned with evolving goals and market demands. This alignment strengthens collaboration between IT teams and business leaders, making the organisation responsive.
4) Improved Value Delivery
CSI focuses on measuring outcomes rather than activities, helping organisations understand whether services are truly delivering value. By using performance data and feedback, teams can prioritise improvements that have the greatest business impact, ensuring IT investments support measurable results.
Challenges Involved in Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
While Continual Service Improvement offers many benefits, implementing it is not always straightforward. Organisations may face some challenges such as:
1) Lack of Clear Objectives
If improvement goals are not clearly defined, teams may focus on the wrong tasks or measure the wrong results. This can waste time and effort. Clear goals help everyone understand what needs to be improved and why.
2) Resistance to Change
Some employees may feel uncomfortable with new processes or changes in the way they work. Change can feel uncertain or risky. Clear communication and strong leadership help teams understand the benefits of new updates and accept such ways of working.
3) Insufficient Resources
Improvement needs time, tools, skilled employees, and budget. If these are not available, progress may slow down. Proper planning and support from management are important to keep CSI efforts moving forward.
Examples and Use Cases of CSI
Continual Service Improvement is useful in many industries apart from IT. Any organisation that wants to improve quality, reduce waste, and serve customers better can apply it. Here are some of the examples and use case of CSI:
1) Information Technology
In IT companies, CSI is used to improve software development and service delivery. Teams analyse recurring issues and system performance to make improvements. For example, an IT company may improve its software release process to launch updates faster and reduce errors.
2) Healthcare
Hospitals and healthcare providers use CSI to improve patient care and daily operations. By studying patient feedback and treatment results, they can improve appointment systems and reduce waiting times.
3) Manufacturing Industry
In manufacturing, CSI helps improve production processes and reduce waste. For example, a car manufacturer might use CSI to reduce the time it takes to switch from making one car model to another. By improving workflow and reducing delays, the company can work faster.
4) Telecommunications
Telecom companies use CSI to improve network reliability and customer support. By analysing service outages and response times, they can reduce downtime and improve connection quality.
Conclusion
Continual Service Improvement is a mindset that encourages organisations to review, measure, and enhance their services continuously. This strengthens service quality and efficiency while keeping services aligned with evolving business goals. As a result, organisations deliver more reliable services, better customer experiences, and stronger operational performance that supports long-term success.
Equip yourself with the tools to optimise service performance with ITIL® 4 Practice Manager (PM) Training – Explore now!
 Have Any Question?
Have Any Question?
 +44 7452 122728
+44 7452 122728






 Back
Back







 44 7452 122728
44 7452 122728




