Table Of Contents


Disasters don’t knock before entering; they crash in, unexpected and uncertain. Whether it is a power outage, cyberattack or sudden system failure, one thing separates chaos from control: a smart, solid plan. That’s where Business Continuity Management quietly steps in, keeping your business calm, collected, and ready for anything.
More than just a backup plan, Business Continuity Management helps businesses stay resilient and prepared for disruptions. In this blog, we’ll explore its key components, how it works, the steps to implement it, the BCM roadmap and the major standards that guide it. Let’s get started!
What is Business Continuity Management?
Business Continuity Management (BCM) is a proactive process that helps organisations prepare for unexpected events like natural disasters, cyberattacks or system failures. It identifies threats, assesses their impact and creates strategies to keep essential functions running during and after disruptions, reducing downtime and protecting assets and reputation.
BCM takes a holistic view by covering people, processes, facilities and technology. It includes planning ahead, training staff, testing plans and improving them regularly. All these efforts form a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) that helps the organisation respond quickly and recover effectively when challenges occur.
Why is Business Continuity Management Important?
BCM is not just about avoiding disaster; it’s about being resilient and adaptable. Here’s why it matters:
1) Minimises Downtime: BCM ensures that business operations continue with little or no interruption.
2) Reduces Financial Loss: Preparedness reduces the cost of disruptions.
3) Protects Reputation: Customers and stakeholders value reliability, especially during crises.
4) Ensures Compliance: Many industries require continuity planning to meet regulatory standards.
5) Boosts Customer Trust: Being ready for emergencies reassures clients and partners.
In short, Business Continuity Management helps your business stay strong when facing the unexpected.
Components of Business Continuity Management (BCM)
These are the core components that help BCM work successfully:
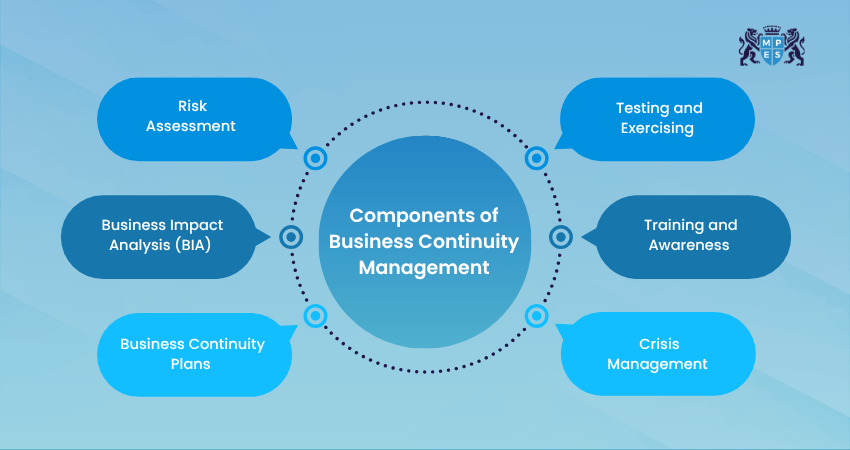
1) Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment is the foundation of BCM. It focuses on identifying potential threats that could disrupt business operations, such as cyberattacks, natural disasters, supply chain failures, or system outages. This step helps organisations understand what might go wrong and prepare strategies to minimise the impact.
2) Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
A Business Impact Analysis determines how each identified risk could affect day-to-day operations. It highlights critical business functions, defines the maximum acceptable downtime, and sets priorities for recovery. This ensures the organisation knows what must be restored first.
3) Business Continuity Plans
Business Continuity Plans outline the specific actions to take during a disruption. They define roles and responsibilities, communication procedures for staff and stakeholders, and detailed steps for recovery and full operational restoration. These plans ensure a structured and coordinated response during emergencies.
4) Crisis Management
Crisis Management focuses on preparing for and handling emergencies effectively. It includes forming a dedicated crisis team, assigning leadership duties, developing communication strategies for employees and the public, and managing the organisation’s reputation during high-pressure situations.
5) Training and Awareness
Training and Awareness ensure that staff understand their roles during a disruption. This involves conducting regular training sessions, promoting awareness across departments, sharing clear emergency procedures, and organising workshops based on specific responsibilities. It builds confidence and readiness.
6) Testing and Exercising
Testing and Exercising help organisations evaluate whether their continuity plans function effectively in real-world situations. This includes running simulations, mock drills, and recovery practice sessions with key teams. The results are reviewed to identify gaps and update the plans, ensuring ongoing improvement and readiness.
How Does Business Continuity Management Work?
Business Continuity Management works as a continuous cycle that helps organisations prepare, respond, and improve over time. Here’s how it works:
1) Understanding Your Business:
Start by identifying your most important services, systems, teams, and tools. Know what your business can’t function without.
2) Identifying Threats:
List all possible events that could interrupt operations. These could include fires, floods, cyberattacks, power outages, or even pandemics.

3) Planning:
For every risk, make a step-by-step plan. This should include how to respond, who will be in charge, and how to keep things running.
4) Testing Plans:
Don’t wait for a real emergency. Run practice drills and scenarios to see how well your plan works and where it needs improvement.
5) Training Staff:
Teach employees what to do in a crisis. Everyone should understand their roles and be confident in taking action.
6) Monitoring and Improving:
Keep checking the plans, especially after major changes in the business. Update regularly so your plan stays useful.
Steps in Business Continuity Management
These steps will help you in developing a robust BCM programme:
1) Initiate the Process
The BCM journey starts by setting clear goals and appointing a Business Continuity Manager or coordinator. It also needs leadership support to secure resources, direction, and commitment. This step forms the foundation for the continuity programme.
2) Identify Critical Operations
Next, you identify which business activities must continue during a crisis. These include essential tasks that directly impact customers, revenue, or core services. Understanding these priorities helps focus efforts where continuity matters most.
3) Conduct Risk and Impact Assessments
Risk and impact assessments help you analyse what could disrupt operations and how severe the consequences might be. This includes estimating potential downtime, financial loss, legal implications, and customer impact. These insights guide your planning decisions.
4) Develop Recovery Strategies
Once risks are clear, recovery strategies are developed to ensure continuity. These may involve using backup systems, enabling remote work, or relying on alternative suppliers. The goal is to have practical options ready to keep the business moving.
5) Create Business Continuity Plans (BCPs)
This step involves creating simple, actionable continuity plans. These documents outline responsibilities, communication methods, response procedures, and recovery steps. The plans must be easy to understand and follow during high-pressure situations.
6) Train and Test
Training ensures employees know their exact roles during a disruption. Regular tests and simulations help determine how well the continuity plans work in practice, revealing strengths and areas for improvement. This keeps everyone prepared.
7) Review and Improve
After each test or real incident, the results are reviewed to identify gaps. Plans are then updated to reflect new risks, lessons learned, and changes in the business environment. This ongoing refinement keeps the BCM programme effective and relevant.
Learn advanced reporting techniques to meet global compliance standards with our Corporate Reporting (CR) Course now!
Business Continuity Management Implementation Roadmap
The BCM Implementation Roadmap outlines key steps to build and maintain a strong continuity plan, starting with leadership support, Risk Analysis, Plan Development, testing, and ongoing improvement.
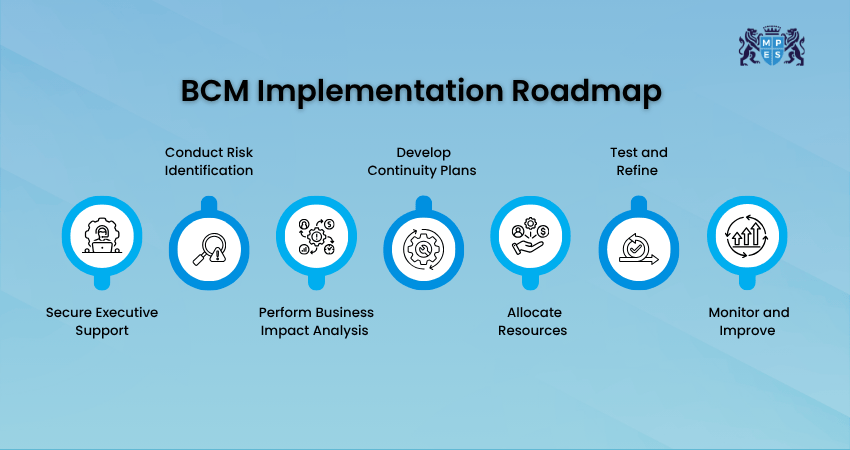
1) Secure Executive Support
The first step is getting strong support from senior leaders. They need to understand why BCM is important, what risks the business may face, and why resources are needed. An executive sponsor should also be appointed to guide the whole process.
2) Conduct Risk Identification
In this step, you work with different teams to find possible threats. You review past incidents, study trends in the industry, look at weak areas in operations, and collect ideas from departments. This helps create a clear list of risks that may affect the business.
3) Perform Business Impact Analysis
A Business Impact Analysis helps you understand how a disruption affects the organisation. It identifies key processes, estimates financial and customer impact, and sets goals for how quickly systems and data should be restored. This helps decide what to recover first.
4) Develop Continuity Plans
Continuity plans are created for different types of incidents such as fire, flood or a cyberattack. These plans include emergency contacts, backup steps, communication methods and details on where staff can work if the main site is not available. They act as a guide during any crisis.
5) Allocate Resources
This step ensures you have what you need to respond during a disruption. It includes assigning roles, forming response teams and providing tools like backup servers or cloud storage. Emergency supplies and communication tools may also be prepared to stay connected.
6) Test and Refine
Testing helps check if the plans actually work. You can run drills and practise different scenarios to see how teams respond. The feedback collected is used to improve and update the plans so they stay effective.
7) Monitor and Improve
BCM needs regular attention to stay useful. Plans should be reviewed often to match new risks or changes in business operations. Staff should also receive continuous training. This helps keep the continuity programme strong and ready for any situation.
Which Business Continuity Management Standards Exist?
Several global and regional standards guide how to implement BCM effectively:

1) ISO 22301: The Global BCM Standard
Set the global standard for BCM by:
1) Providing a structured framework for continuity planning
2) Identifying potential threats and assessing business impact
3) Establishing strategies to maintain essential operations during disruptions
4) Requires regular reviews and encourages continuous improvement.
2) BSI-Standard100-4 & 200-4: Public Sector and IT Guidance
Support the public and IT sectors by:
1) Offering guidelines from the German Federal Office for Information Security
2) Focusing on risk management, IT continuity, and recovery planning
3) Helping align security requirements with operational continuity
4) Encouraging tailored BCM strategies for government and tech environments
3) NIS-2 Directive: EU Cyber Resilience Regulation
NIS 2 strengthens cybersecurity and BCM across critical sectors in the EU
1) Requires EU member states to enforce strong cybersecurity measures
2) Promotes BCM in sectors like healthcare, energy, and transport
3) Mandates incident reporting and regular risk assessments
4) Improves digital and operational resilience for essential services
4) DORA: Digital Operational Resilience Act
Protect financial services from digital threats by:
1) Enforcing rules for handling ICT-related disruptions in the EU
2) Requiring continuous risk monitoring and testing of resilience
3) Managing third-party risks from IT service providers
4) Promotes a unified approach to digital operational resilience across financial services.
Conclusion
Business Continuity Management is important for keeping your organisation steady in the face of disruption. By planning, identifying risks and regularly testing strategies, you ensure minimal downtime and faster recovery. A strong continuity strategy not only protects operations but also builds long-term resilience, customer trust and confidence in your capability to manage the unexpected.
Build leadership capabilities to thrive in competitive finance environments. Join our ACA Advanced Level Training now!
 Have Any Question?
Have Any Question?
 +44 7452 122728
+44 7452 122728






 Back
Back







 44 7452 122728
44 7452 122728





