Table Of Contents


Business Process Management (BPM) is the art of refining how organisations work behind the scenes, turning scattered tasks into smooth workflows. As the business world turns up its pace, BPM acts as the backbone of operational excellence, making sure that businesses stay agile and competitive.
This blog explores how Business Process Management can help your business map, analyse and improve its everyday processes so your team can work smarter and with fewer errors. So read on and embrace this proven ingredient to lasting business success!
What is Business Process Management (BPM)?
Business Process Management is a method for analysing, planning, and improving the way a business operates. It looks at full processes from start to finish, especially those that are repeated regularly. Unlike task or Project Management, which handles one-time activities or individual tasks, BPM focuses on improving the entire process to make it more efficient and effective.
By constantly improving their processes, organisations can make their work smoother, faster, and more cost-effective. Business Process Management tools facilitate this process by leveraging Data Analysis, real-time tracking, and intelligent decision-making capabilities. These tools bring together people, systems, and information to reach business goals more efficiently.
Why is Business Process Management Important?
Business Process Management (BPM) is essential because it helps businesses operate more smoothly, efficiently, and with greater flexibility. It examines how work is performed, identifies areas for improvement, and helps minimise errors, delays, and inefficiencies.
By enhancing these everyday processes, companies can save time, reduce costs, maintain high customer satisfaction, and quickly adapt to changing market conditions. This continuous improvement supports business growth and helps maintain a competitive edge. We’ll explore BPM’s benefits in detail later in this blog.
Different Types of BPM
Business Process Management can be categorised into different types based on the type of work it focuses on. Let's dive in:
Integration-centric BPM
a) This type of BPM focuses on processes that rely mainly on systems and technologies.
b) It involves minimal human interaction or decision-making throughout the workflow.
c) The primary goal is to automate the data flow between various systems.
d) It connects tools such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), marketing automation, and finance systems.
e) Application Programming Interface (APIs) or service buses are used to integrate various applications smoothly.
Human-centric BPM
a) This type of BPM is centred around tasks that require human decision-making or action.
b) It is designed for processes that require human input, such as approvals, reviews, and customer service.
c) The workflows are designed to be user-friendly and flexible, accommodating various task types.
d) It allows users to interact with, reassign, pause, or complete tasks as needed.
e) Features like alerts, notifications, and flexible task handling often support these processes.
Document-centric BPM
a) This type of BPM manages processes that rely heavily on documents such as contracts, forms, invoices, and reports.
b) It focuses on tasks like drafting, reviewing, approving, signing, storing, and tracking document versions.
c) The process ensures that documents are properly handled, organised, and shared throughout their lifecycle.
d) It helps improve accuracy by reducing errors and maintaining consistent document standards.
e) This type of BPM also ensures compliance by maintaining up-to-date records and making them easy to audit.
Bridge the final gap between financial theory and practice and reach the pinnacle of the ACA Qualification! Sign up for our Case Study (CS) Training now!
Business Process Management Lifecycle
Business Process Management lifecycle is a systematic approach for helping organisations understand, improve, and optimise their processes. Let’s look at the elements.
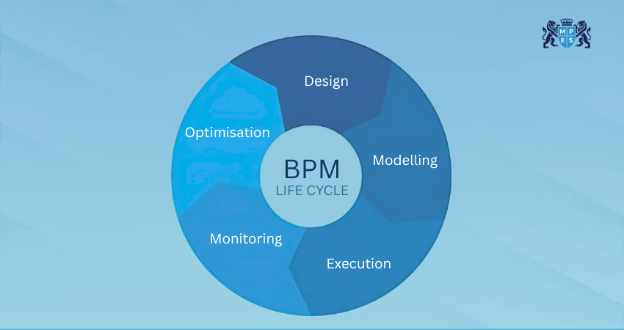
1) Design
This process is redesigned to achieve better performance. Here, a simulation engine helps to compare different optimisation options and predict outcomes. Also, visual designs help stakeholders understand updated workflows, making collaboration easier and transitions smoother.
2) Modelling
Once issues are clear, the ideal process can be modelled. This includes visualising how tasks should flow and how data must move between teams. Modelling enables organisations to test improvements, such as system integration. This makes sure the updated workflow is practical and efficient.
3) Execution
This stage introduces automation and changes to how teams are approaching work. This shows why change management is essential for maintaining seamless operations in an organisation. Here, clear communication, support, and training help to reduce resistance and ensure everyone follows the workflow correctly.
4) Monitoring
Ongoing monitoring ensures the process is performing as expected. If issues reappear or bottlenecks arise, adjustments can be made accordingly. Here, automation plays a crucial role since it reduces manual work, improves speed, and brings in efficiency and customer satisfaction.
5) Optimisation
Optimisation focuses on improving the process, even after its implementation. This involves identifying new inefficiencies and introducing Business Process Automation (BPA) to reduce manual work and improve speed. These enhancements keep processes accurate, efficient, and aligned with changing business requirements.
Step into the pinnacle of professional excellence with our ACA Advanced Level Course- Sign up now!
Use Cases of Business Process Management
Business Process Management helps make workflows more organised and efficient by removing delays and confusion. Here are some examples of how it’s used:
1) Finance
Companies can use Business Process Management to create standard templates for purchase orders, making it faster for teams to request software or hardware. They can also set up custom steps for unique situations.
2) Order Fulfilment
Businesses use Business Process Management to run their order systems better. It helps manage special offers, take orders, and handle deliveries, making the whole process more focused on the customer and more valuable for the business.
3) Customer Service
Customer service teams can utilise BPM to identify common questions and delegate them to chatbots, particularly during peak periods. It also helps use call and chat data to make answers more personal and automate tasks further.
4) Content Distribution
Media companies use BPM to automate a multitude of tasks, ranging from creating content to sending it out. It can connect with tools that manage content, rights, schedules, and work orders.
5) Streamlining HR Activities
HR departments use BPM to manage forms and approvals more smoothly. It helps them with tasks including hiring, staff exits, performance reviews, leave requests, and timesheets.

6) Optimising Banking Processes
Banks use BPM to speed up loan processing. It helps gather information from applicants, employers, and credit agencies quickly and accurately, making it easier to decide who qualifies for a loan.
Master the art of financial storytelling with our comprehensive Corporate Reporting (CR) Course - Register now!
Benefits of Business Process Management
Here are among the many benefits that Business Process Management can offer to senior decision-makers:
1) Improves Visibility
a) BPM gives clear visibility into how different processes work within the organisation.
b) This visibility enables leaders to see how each process contributes to the overall business goals.
c) It allows decision-makers to identify areas that need improvement or streamlining.
d) Understanding process performance helps align operations with strategic objectives.
2) Customer Experience
a) A Business Process Management suite helps eliminate repetitive tasks by automating routine work.
b) It improves access to information, making it easier for employees to find what they need.
c) By reducing distractions, employees can put all their focus on their work and customers.
d) This results in improved customer satisfaction and improved service quality.
e) Clear workflows make onboarding easier, enabling new employees to learn more quickly.
3) Aligns Processes with Strategy
a) Business Process Management helps align day-to-day business processes with the organisation’s overall strategic objectives.
b) It involves mapping processes to gain a clear understanding of how work is done.
c) BPM identifies inefficiencies and bottlenecks that may hinder performance.
d) By streamlining workflows, BPM ensures that operations support and drive strategic goals.
4) Less Dependency on Development Teams
a) Many BPM tools offer low-code or no-code capabilities, reducing reliance on developers.
b) This allows business users with minimal technical skills to build and manage processes.
c) Users can be trained and onboarded quickly, making adoption easier across teams.
d) It helps increase automation throughout the company by enabling broader participation.
5) Improved Process, Optimisation, and Standardisation
a) Business Process Management helps standardise processes throughout the organisation.
b) It helps make sure that tasks are carried out consistently and efficiently.
c) This is especially beneficial for businesses operating across multiple locations.
d) Additionally, it supports compliance with industry regulations and standards.
6) Stronger Governance, Compliance, and Risk Management
a) BPM helps industries that must follow regulatory rules ensure that every step in a process is completed properly.
b) It helps ensure that all actions are documented for audits and compliance checks.
c) BPM also helps identify risks within business processes before they become major issues.
d) It supports risk mitigation by improving control, oversight, and accountability.
From ledgers to leadership, Financial Accounting is your first step towards excellence! Sign up for our Financial Accounting (FA) Course now!
Challenges of Business Process Management
Business Process Management is challenging because it requires aligning diverse stakeholders and adapting to constant changes in technology, markets, and regulations. Organisations will often struggle with the following key challenges in Business Process Management:
1) Unclear Processes
When workflows are unclear or not properly documented, teams may become confused, repeat tasks, or experience delays. This slows down progress and makes it hard to deliver consistent results. Clear steps help everyone stay on track and work efficiently.
2) Team Responsibility Gaps
If it’s not clear who is responsible for what, tasks can be missed, duplicated, or delayed. This can lead to strained relationships between departments and hinder teamwork. Defining roles clearly helps avoid confusion and boost collaboration.
3) Struggling with Rapid Changes
Processes that are too rigid make it hard for companies to keep up with market changes or customer needs. This can hurt competitiveness. Flexible processes help businesses respond quickly and stay ahead.
4) IT Dependencies Limit Flexibility
Outdated or overly complicated IT systems slow things down and require too much effort to update. This can delay progress and waste resources. Simplifying systems makes changes easier and faster to manage. 
5) Lack of Visibility Into Operations
Without up-to-date data or clear performance tracking, businesses can’t easily spot problems or measure results. This leads to poor decisions and missed opportunities. Visibility helps leaders make smarter, faster choices.
6) Compliance and Regulatory Hurdles
When processes aren’t regularly checked or don’t include compliance steps, it’s easy to miss important rules. This can result in penalties or damage to reputation. Regular reviews and checks keep processes compliant and secure.
Shape smarter business decisions with Business Management (SBM) Training – Register now!
What is the Future of Business Process Management?
The future of Business Process Management is evolving as technology and the workplace change. With digital operations, remote work and AI-driven tools, organisations are modernising how they operate. Also, low-code platforms and citizen developer solutions are making BPM more accessible, thus enabling more employees to improve workflow.
As automated process mining, real-time modelling and process simulation help detect issues proactively and Generative AI shapes workflows, Business Process Management is shifting toward continuous innovation. The future will be smarter automation, flexibility and constant improvement to prepare organisations for change and job competitiveness.

Business Process Management Examples
Here are some common examples of BPM:
1) Order Fulfilment: This involves handling customer orders from start to finish, ensuring they’re accurate and delivered on time.
2) Customer Refunds: This involves managing returns and refunds by checking the request, processing the payment, and keeping records up to date.
3) Shipping: This involves taking care of how products are packed, labelled, tracked, and sent to customers.
4) Invoicing: It involves creating and sending bills to customers, ensuring everything is accurate, and tracking payments.
5) Customer Onboarding: This involves helping new customers get started by offering support, information, and guidance to build a strong relationship.
6) Account Management: This involves looking after existing customers, solving any problems, meeting their needs, and encouraging long-term loyalty.
Conclusion
Business Process Management empowers organisations to work smarter, deliver faster, and create valuable experiences for customers and employees. Continuous reviewing and refining processes help businesses to improve productivity and stay adaptable in the face of change. With emerging technologies and advancements in automation, BPM has become essential for sustaining long-term success and preparing companies for the future.
Looking for a gateway to elite financial mastery? Our ACA Advanced Level Training will lead the way - Sign up now!
 Have Any Question?
Have Any Question?
 +44 7452 122728
+44 7452 122728






 Back
Back







 44 7452 122728
44 7452 122728





