Table Of Contents


Have you ever wondered what those “amounts owed” on a company’s balance sheet really mean? That’s where Liabilities come in. But What are Liabilities? They represent what a business or person needs to pay back, whether it’s loans, bills, or other dues. Knowing about Liabilities helps you stay in control of your money and avoid unwanted surprises.
Whether you’re managing a business or just learning about finance, understanding Liabilities is a big step toward smarter money decisions. In this blog, we will discuss What are Liabilities, how they work, and why they matter.
Table of Contents
What are Liabilities?
How Liabilities Work?
Types of Liabilities
Importance of Understanding Liabilities
Differences Between Current and Non-current Liabilities
Liabilities vs Assets
Liabilities vs Expenses
Liability Examples
Conclusion
What are Liabilities?
Liabilities are financial obligations a business owes to others. These can be bills, loans, or any other debts that must be paid in the future. Liabilities are a normal part of running a business and are listed on the balance sheet. They show what the company is responsible for paying.
For example, if a bakery buys flour and sugar from a supplier and agrees to pay later. That unpaid amount becomes a liability. Or, if the bakery takes a loan to buy a new oven, the loan is a liability until it’s fully paid. Knowing your Liabilities helps you plan your money and avoid problems.
How Liabilities Work?
Here are the main ways Liabilities work in a business and affect everyday operations:

1. Recording Liabilities in Financial Statements
Liabilities are listed on the balance sheet to show what the business owes. They are usually grouped into short-term and long-term based on when they are due. Recording them properly helps give a clear view of financial health.
Show what the business owes to others
Help track payment deadlines and due dates
Important for accurate financial reporting
2. Impact on Business Operations
Liabilities affect daily decisions like spending, borrowing, and investing. If Liabilities are too high, the business may face financial stress. Managing them well helps keep the business running smoothly.
Guide decisions on loans and expenses
Help maintain good relationships with lenders
Affect the ability to grow and expand
3. Settling Liabilities Over Time
Businesses must pay off Liabilities using cash or other assets. Some are paid quickly, like bills, while others, like loans, take years. A good plan ensures that payments are made on time.
Plan ahead for regular payments
Avoid penalties or interest charges
Maintain trust with suppliers and creditors
Types of Liabilities
Here are the main types of Liabilities businesses often deal with:
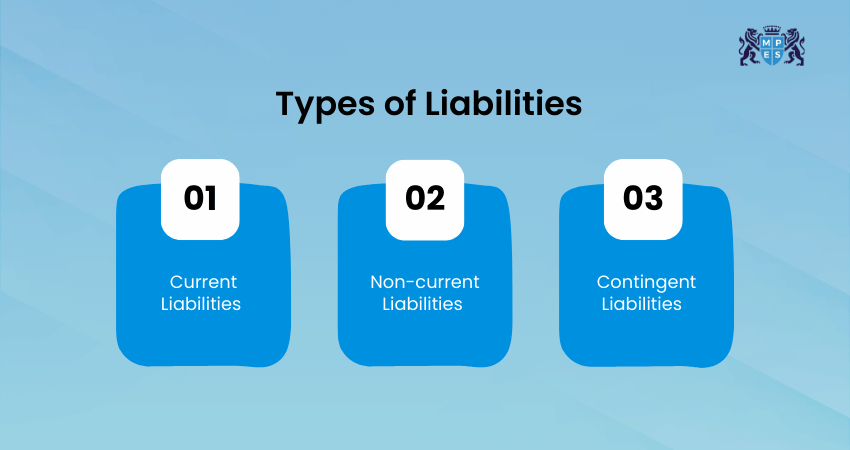
Current Liabilities
These are debts or obligations a business must pay within a year. These are usually short-term payments like bills, wages, or taxes. Managing them well is important to keep daily operations running smoothly.
Examples include unpaid bills, rent, or utility costs
Salaries and wages that are due soon
Short-term loans or credit that must be repaid quickly
Non-current Liabilities
These are debts that don’t have to be paid right away. These are usually due after more than a year, such as business loans or long-term leases. They help fund big projects and long-term goals.
Long-term business loans and mortgages
Bonds or financial agreements due in future years
Leases that last longer than 12 months
Contingent Liabilities
Contingent Liabilities are possible debts that may happen in the future. They depend on certain events, like a lawsuit or guarantee. These don’t always become real Liabilities, but businesses must still keep track of them.
Legal claims or pending court cases
Guarantees made for other people’s loans
Environmental clean-up costs that may come up
Enhance your banking expertise with Business Planning Banking (BPB) Course - join now!
Importance of Understanding Liabilities
Some of the reasons why knowing about Liabilities is important for any business include:
Financial Health
Helps you understand how much your business owes
Shows the balance between assets and debts
Makes it easier to track business growth
Keeps your finances clear and organised
Managing Cash Flow
Helps plan when to pay bills and loans
Avoids running out of money unexpectedly
Supports better budgeting and spending
Makes daily operations smoother
Tax Considerations
Some Liabilities may be tax-deductible
Helps prepare accurate tax returns
Reduces the risk of tax penalties
Keeps records ready for audits
Risk Mitigation
Shows how much risk your business carries
Helps avoid taking on too much debt
Makes it easier to plan for tough times
Encourages smarter financial decisions
Take control of your finances with our Business Planning Tax (BPT) Course - Join today!
Differences Between Current and Non-current Liabilities
Here are the key differences between them:
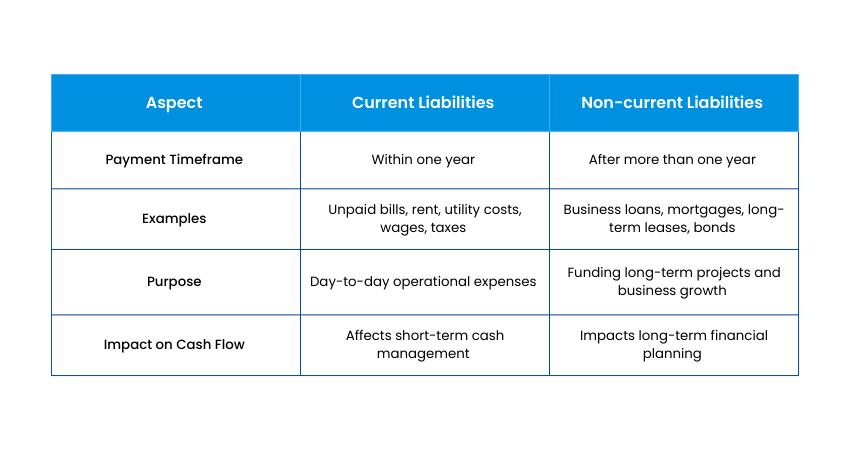
1. Time of Repayment
Current Liabilities are debts that must be paid within a year. On the other hand, non-current Liabilities are long-term and usually paid over several years. This difference affects how a business plans its short-term and long-term finances.
2. Impact on Cash Flow
Current Liabilities affect daily and monthly cash needs. In contrast, non-current Liabilities allow for planning over a longer period. Businesses must balance both to stay financially healthy.
3. Examples and Usage
Examples of current Liabilities include utility bills and short-term loans. On the other hand, non-current Liabilities include mortgages or long-term lease obligations. Both types are used to fund operations but have different repayment terms.
Liabilities vs Assets
Here’s how Liabilities differ from assets in a business:
1. What They Represent
Assets are things a business owns that bring value, like cash or equipment. Liabilities, on the other hand, are amounts the business owes to others. This means assets add value while Liabilities represent future payments. A strong business tries to grow assets and manage Liabilities wisely.
2. Financial Position
Assets improve a company’s financial strength. In contrast, Liabilities show how much the company must pay. Having more assets than Liabilities is a sign of good financial health. This balance helps banks and investors judge a company’s success.
3. Examples
Cash, property, and inventory are common assets. On the other hand, loans and unpaid bills are Liabilities. Both appear on a balance sheet but in opposite sections. Understanding them helps track what you own versus what you owe.
Liabilities vs Expenses
Let’s look at how Liabilities are different from expenses:
1. Timing and Nature
Liabilities are unpaid debts or obligations that stay on the books until cleared. Expenses, on the other hand, are costs that are recorded when they happen. So, Liabilities remain as balances while expenses are used up immediately. An expense becomes a liability if it isn't paid right away.
2. Financial Reporting
Expenses show up on the income statement to measure profit. In contrast, Liabilities are reported on the balance sheet as amounts owed. Each plays a different role in understanding a company’s financial health. Keeping both updated helps track performance and financial duties.
3. Examples
Examples of expenses include rent, salaries, and utility costs. On the other hand, Liabilities include unpaid rent or pending salaries. So, an expense can become a liability if it's not paid yet. It’s important to pay on time to avoid increasing Liabilities.
Gain clarity in financial management with our ACA Professional Level Course - Join today!
Liability Examples
Here are the examples of common Liabilities found in business and daily life:
- Bank Loans: Money borrowed from a bank that must be repaid with interest.
- Accounts Payable: Bills or invoices owed to suppliers for goods or services.
- Credit Card Debt: Outstanding balances owed on business or personal credit cards.
- Wages Payable: Salaries that are owed to employees but not yet paid.
- Taxes Payable: Tax amounts due to the government that haven’t been paid yet.
- Mortgage Loans: Long-term loans taken out to buy property or buildings.
- Customer Deposits: Money received in advance for goods or services yet to be delivered.
- Utility Bills: A common household liability where payments are due for services like water, electricity, or gas.
Conclusion
We hope this blog helped you understand What are Liabilities and why they matter in business. Knowing your Liabilities helps you manage money better, avoid risks, and keep your business stable. Whether it's loans, bills, or taxes, keeping track of what you owe is a key part of staying financially healthy. Always stay informed and organised to make smart and safe financial decisions.
Strengthen your financial decisions with our Financial Accounting and Reporting (FARI) Course - Join today!
 Have Any Question?
Have Any Question?
 +44 7452 122728
+44 7452 122728






 Back
Back







 44 7452 122728
44 7452 122728





