Table Of Contents


In the complex financial ecosystem, the noblest goal is to maintain a fair balance between wealth and responsibility. A prime example is the principle that as income increases, the tax rate also rises. That's the heartbeat of Progressive Taxation; a system built on fairness that eases the burden on low earners while asking more from those who can afford it.
In this blog, we’ll unpack What is Progressive Tax, explore its numerous examples and weigh its pros and cons in a simple way. So, let’s dive in and decode the logic behind the laddered tax system and how it strengthens societies and nations!
Table of Contents
What is Progressive Tax?
How Does a Progressive Tax Work?
Advantages of Progressive Tax
Disadvantages of Progressive Tax
Progressive vs Regressive Tax: Key Differences
Progressive Tax Examples
Conclusion
What is Progressive Tax?
A Progressive Tax is a taxation system where individuals with higher incomes pay a larger percentage of their earnings in taxes compared to those with lower incomes. This means that someone with a higher income will pay more tax than someone with a lower income. It’s designed to make taxes fairer by asking those who can afford it to contribute more to public services.
The goal of a Progressive Tax is to lessen the financial gap between the rich and poor. The money collected helps pay for things like schools, hospitals and roads. Some people think it may stop high earners from working harder, while others believe it helps create a fairer society by sharing the tax burden based on income levels.
How Does a Progressive Tax Work?
A Progressive Tax system works by applying increasing tax rates as income rises. Governments divide income into brackets, each with its own marginal tax rate, for example, 10%, 12%, 22%, etc. You pay the lower rate on income within the first bracket, then the next higher rate on the portion above that, and so on.
This structure ensures that only the income in each bracket is taxed at its specific rate, not your total income at the highest rate. This mechanism strikes a balance between fairness and revenue generation.
Advantages of Progressive Tax
There are several benefits of the Progressive Tax model. Let’s explore them in detail:

1. Better Funded Programmes
Progressive Taxes allow high earners to fund key government programmes and services.
Additional revenue supports infrastructure projects, such as roads and bridges.
It helps finance social programmes aimed at public welfare.
These investments improve the living conditions across society.
Lower-income individuals gain greater access to opportunities for growth and well-being.
2. Increased Tax Money
Progressive Tax models can help the government generate higher overall tax revenue.
Individuals moving into higher tax brackets pay increased percentages of their income.
This system adjusts the contributions based on income growth.
Unlike flat or Regressive Taxes, it allows for greater collection without burdening low earners.
3. Fair Distribution
Individuals are taxed based on their income level, making the system more equitable.
Lower-income individuals pay less tax, easing their financial pressure.
With more disposable income, low earners can spend more on essentials like food and clothing.
Greater consumer spending by lower-income groups helps stimulate the overall economy.
Lay the groundwork for a global finance career. Sign up for our ACCA Foundations Training now!
Disadvantages of Progressive Tax
Despite the many benefits, the Progressive Tax system is not without some drawbacks. Let's examine them:
1. Increasing Administrative Costs
Varying tax rates can increase administrative workload for government agencies.
Managing multiple tax bands requires more complex processing and oversight.
Uniform tax rates are simpler and less time-consuming to handle.
Smaller incremental tax changes may demand more manual calculations.
This can result in higher operational costs and increased resource utilisation.
2. Encouraging Overseas Investments
High Progressive Taxes can drive individuals and businesses to seek lower-tax countries.
This can result in increased capital flight and reduced domestic investment.
Dramatic tax hikes may prompt wealthy individuals to explore foreign investment opportunities.
Sudden rises in tax rates can make local markets less attractive.
Businesses may relocate to regions with more stable, moderate taxation.
3. Discouraging People From Pursuing Wealth
High taxes on the wealthy might discourage individuals from increasing their income.
Some may seek loopholes or tax credits to remain in lower tax brackets.
This behaviour can reduce motivation to earn more.
It creates a perception that earning more leads to fewer net benefits.
The system may seem to penalise financial success.
Progressive vs Regressive Tax: Key Differences
Here are the key differences between Progressive Tax and Regressive Tax:
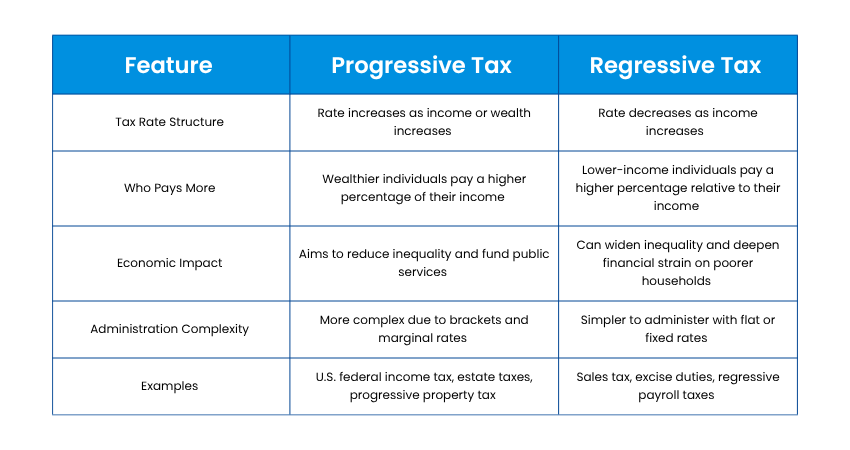
Progressive Tax Examples
As mentioned above, Progressive Taxes grow with your income, fair, balanced, and designed to ease the burden on lower earners. Now, let’s explore the various examples of Progressive Tax that show how this system works.
1. Investment Taxes
Investment-related taxes can also be progressive. As individuals engage in more investment activity, their tax obligations may rise. This includes taxes on income from rental properties or other financial assets. Depending on the jurisdiction, certain deductions or reliefs may be available to offset some of these taxes.
2. Value Added Tax (VAT)
VAT can sometimes have progressive elements. It applies different tax rates based on the type or value of goods. For example, essential items like groceries and children's clothing often have lower tax rates, while luxury items such as electronics or high-end cars may be taxed at higher rates. In the UK, the standard rate of VAT is currently 20% but you can avail reduced rates of 5% on goods such as child car seats, domestic fuel or power and mobility aids.
3. Inheritance Tax
In some regions, inheritance tax is structured progressively. The tax rate usually increases with the size of the inheritance. For example, inheritances below a certain threshold may be tax-free, but larger amounts are taxed at higher rates.
The standard Inheritance Tax rate in the UK is 40% and is only charged on the part of your estate that’s above the threshold. This resembles the U.S. estate tax, where estates valued below $5.3 million are exempt from taxation, while amounts above that threshold face a 40% tax rate.
Decode the UK tax system like a pro. Our Taxation (TX-UK) Training will equip you with the skills to master tax law - Sign up now!
4. Income Tax
Income tax in multiple locations is typically progressive, as it often varies with individual earnings. Here are the common tax bands and rates:
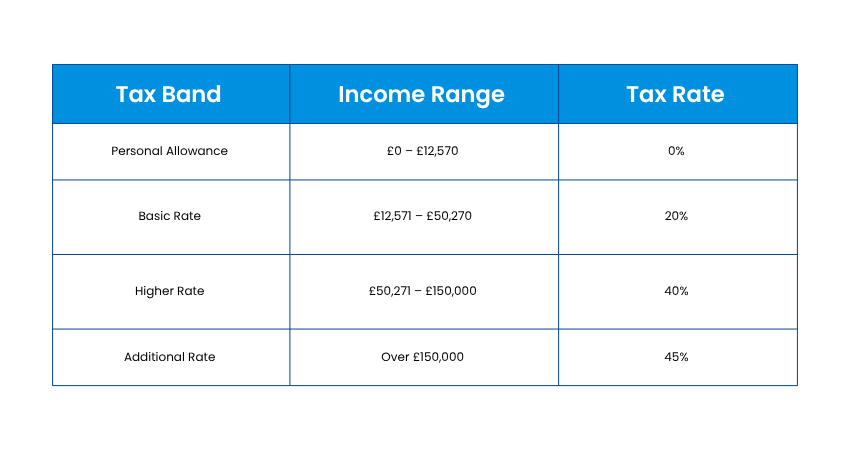
5. Capital Gains Tax and Stamp Duty
Capital gains tax often targets higher earners who sell investments or property for a profit. It becomes more significant for those with substantial assets. Stamp duty is another example of tax on property transactions. In this case, properties sold for less than £125,000 are tax-free, but the tax rate increases for higher-valued properties, making it progressively more costly as the sale value rises.
Conclusion
More than just a system, Progressive Tax is a tool for fairness. Adjusting tax rates based on income helps balance economic inequality and fund vital public services. While it has drawbacks, its benefits in supporting social equity and government revenue make it a widely used approach. Understanding What is Progressive Tax and how it works is key to making informed financial and civic decisions.
Looking to sharpen your expertise in complex tax planning? Our Advanced Taxation (ATX) Training will turn you into the tax expert everyone trusts - Sign up now!
 Have Any Question?
Have Any Question?
 +44 7452 122728
+44 7452 122728






 Back
Back







 44 7452 122728
44 7452 122728





