Table Of Contents


Think about how you handle your monthly salary, setting aside money for bills, savings, and a little fun. Now imagine scaling that process up to a company managing millions. This is where Financial Management comes in. It helps businesses spend wisely, earn effectively, and stay prepared for whatever the future brings.
In this blog, we’ll explain What is Financial Management is and why it matters. We’ll also explore its types, main functions, scope, and goals, using examples to keep everything simple, clear, and relatable.
What is Financial Management?
Financial Management refers to the vital process of planning, organising, guiding and controlling all financial activities in a business or organisation. It involves applying core management principles to manage a company’s funds and assets effectively. This function is essential for maintaining financial stability and guiding sound decision-making.
Main Objectives of Financial Management:
1) Making sure the business has enough funds to run smoothly
2) Giving good returns to shareholders on their investments
3) Using available funds in the best and most efficient way
4) Finding safe and profitable investment opportunities for growth
Why is Financial Management Important?
The significance of Financial Management lies in the fact that it helps businesses plan, control, and use money properly. Without it, even successful companies can lose money or fail. It makes sure a business has enough funds to work smoothly, invest wisely, and reach both short-term and long-term goals.
Here’s why Financial Management matters:
1) Keeps the Business Running: Ensures there’s enough money to pay bills, salaries, and other expenses.
2) Helps in Making Decisions: Provides clear information to choose the best financial options.
3) Manages Risks: Prepares the company for unexpected problems or emergencies.
4) Increases Profits: Reduces extra costs and improves efficiency.
5) Supports Growth: Makes money available for expansion and new opportunities.
Become a taxation expert with our Taxation (TX-UK) Training – Register today!
Functions of Financial Management
Financial Management performs several key functions to ensure smooth operations. Let’s explore them in detail:
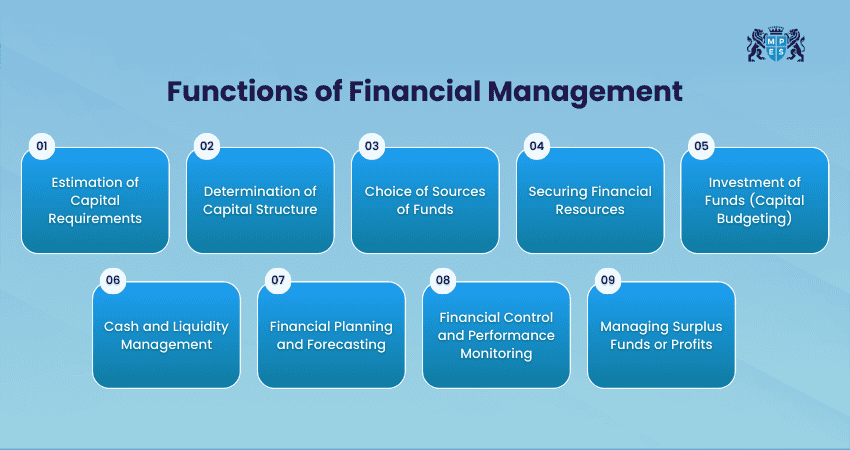
1) Estimation of Capital Requirements
Assessing the required capital is a key responsibility within Financial Management. It helps determine the amount of money or assets an organisation needs to meet its goals. Here are some techniques for Assessing Required Capital:
1) Estimating Cash Flows
Financial Managers forecast future earnings and expenses by analysing current results and expected market changes. They use techniques like Internal Rate of Return (IRR), Net Present Value (NPV) and payback period to judge whether upcoming projects will be profitable.
2) Evaluating Capital Availability
Managers examine interest rates, inflation, and taxes to understand the cost of raising funds. They also compare sources such as debt, equity and retained profits, evaluating how each affects control, financial risk, and long-term cost.
3) Achieving the Right Balance
Financial Managers aim to balance profitability, liquidity and risk. They determine the optimal capital amount and mix that supports growth while ensuring financial stability and meeting stakeholder expectations.
2) Determination of Capital Structure
This is a core function of Financial Management and involves deciding the proportion of debt and equity used to finance operations. This mix influences profitability, liquidity, solvency and overall financial risk. Financial Managers aim to choose an optimal structure that maximises organisational value and minimises cost of capital, while considering ownership dilution, tax benefits, interest obligations and financial flexibility.
Become a taxation expert with our Taxation (TX-UK) Training – Register today!
3) Choice of Sources of Funds
Once capital needs are determined, Financial Managers must select suitable sources of finance. Options include equity, loans, retained earnings or external investors, each differing in cost, repayment terms, ownership dilution and risk. Managers compare these factors and choose sources that align with financial goals, support growth and maintain manageable risk for the organisation.
4) Securing Financial Resources
After selecting suitable funding sources, the next step is securing the required funds. This involves preparing financial statements and proposals that justify funding needs and support decision-making. Financial Managers negotiate terms such as interest rates, repayment duration and investment conditions to ensure funds are obtained on time, at a favourable cost, and with minimal financial risk.
5) Investment of Funds (Capital Budgeting)
Fund investments involve giving organisational funds to different financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. Investing funds helps organisations earn additional income and grow their capital base. Financial Managers must decide which securities to invest in, the appropriate investment amount, the best timing for investment and when to exit.
6) Cash and Liquidity Management
Cash Management focuses on handling cash and highly liquid assets efficiently. Its goal is to ensure adequate liquidity for operational expenses and future opportunities. Financial Managers forecast inflows and outflows, prepare cash budgets and maintain policies to support smooth payments and working capital needs. This ensures uninterrupted operations and prevents liquidity shortages.
7) Financial Planning and Forecasting
Financial planning and forecasting involve predicting revenue, expenses and financial trends to support informed decision-making. Financial Managers analyse financial statements such as the income statement, balance sheet and cash flow to assess short-term and long-term performance. Using methods like ratio and variance analysis, they develop projections that support budgeting, resource planning and long-range financial strategy.
8) Financial Control and Performance Monitoring
Financial control ensures the accuracy, transparency and compliance of financial information. It includes approval systems, reconciliations, audits and segregation of duties to prevent fraud or errors. Monitoring these controls often works alongside analysing Accounting Ratios, helping maintain accountability, detect issues early and ensure that funds are used responsibly according to policy and regulatory requirements.
9) Managing Surplus Funds or Profits
Managing surplus funds involves deciding how profits are allocated once obligations are met. Financial Managers may distribute dividends, reinvest earnings, or repay existing debt. Effective allocation supports shareholder value, organisational growth and financial stability, while considering taxation and retention needs for future expansion.

Types of Financial Management
Financial Management has different types, each focusing on specific aspects of a company’s finances. Now, we'll discuss them along with examples of Financial Management to help you understand how they work in real situations.

1) Capital Budgeting
Capital budgeting helps businesses plan by deciding where to invest money for the best returns. Financial Managers analyse different projects or investments to check if they’ll be profitable and help the organisation grow.
Example:
A retail brand decides whether to spend £50,000 on opening a new store or upgrading its online platform. Capital budgeting helps pick the better option.
2) Capital Structure
Capital structure is about how a company funds its operations and growth. Businesses use a mix of equity (owners’ money) and debt (borrowed money). A healthy balance ensures financial stability and reduces risks.
Example:
A construction company finances a new project by using 60% equity and 40% loans, keeping repayment manageable while still funding expansion.
3) Working Capital Management
This type focuses on day-to-day financial operations. It ensures the organisation always has enough money to pay employees, buy raw materials, and cover short-term expenses. It involves managing:
a) Cash on hand
b) Inventory levels
c) Other quick assets that can be sold in emergencies
Example:
A bakery makes sure it has enough cash to pay workers, buy ingredients, and keep operations running smoothly.
4) Revenue Cycle Management
Revenue Cycle Management tracks how and when a company earns money from selling products or services. With many businesses now using subscription-based models or offering services “as a service,” income is spread out over time instead of coming in all at once.
Example:
A software company charges a monthly subscription. Revenue is recognised every month as customers pay, known as Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR).
Transform your reporting confidence with our Financial Reporting (FR) Training - Join now!
Functions of Financial Management
Financial Management performs several key functions to ensure smooth operations:
1) Estimation of Capital Requirements
Assessing the total funds needed to start, operate, and expand the business, including fixed and working capital, ensuring adequate resources for the company’s objectives. Proper estimation prevents underfunding or excess borrowing that could harm stability.
2) Determination of Capital Structure
Deciding the right mix of debt and equity to finance the business, minimising cost while maximising shareholder value. A balanced structure also reduces financial risk and ensures long-term sustainability.
3) Choice of Sources of Funds
Selecting suitable funding sources such as loans, equity, or bonds, based on cost, risk, and availability. This choice directly affects the company’s flexibility, control, and overall financial health.
4) Investment of Funds (Capital Budgeting)
Allocating capital to profitable projects after analysing risks and returns to maximise long-term growth. Good investment decisions boost competitiveness and support innovation.
5) Cash and Liquidity Management
Ensuring sufficient liquidity for day-to-day operations, payments, and contingencies while optimising cash usage. It also helps the business avoid cash shortages that can interrupt operations.
6) Financial Control and Performance Monitoring
Tracking financial performance using budgets, forecasts, and ratios to ensure effective fund utilisation and cost control. This function highlights inefficiencies early and supports timely corrective action.
7) Financial Planning and Forecasting
Projecting future financial needs and preparing strategies to meet those requirements for smooth business operations. Accurate forecasting allows businesses to stay prepared for both opportunities and risks.
8) Dividend Decisions
Deciding how to distribute profits as dividends or retain earnings for reinvestment in the business. Balanced dividend policies build investor confidence while fuelling future growth.
9) Risk Management
Identifying, assessing, and mitigating financial risks to safeguard company assets and ensure stability. It protects the business from market uncertainties and unexpected losses.
Scope of Financial Management
The scope of Financial Management covers the key areas of managing a company’s money. It helps businesses plan effectively, control expenses, and prepare for the future. Here are the main areas explained:
1) Planning
Planning is about deciding how much money the company needs and how to use it. The Financial Manager makes sure there is enough money to:
a) Run the business smoothly
b) Start new products or services
c) Handle unexpected problems
Planning also covers different parts like big investments, employee expenses, and day-to-day costs.
2) Procedures
Procedures are rules and steps for handling money. They explain how to manage:
a) Payments and invoices
b) Financial reports
c) Who approves and makes financial decisions
Clear procedures improve accuracy, security, and accountability in financial operations.
3) Budgeting
Budgeting means deciding how to spend the company’s money. It helps control costs like:
a) Salaries
b) Rent or office expenses
c) Buying raw materials
d) Employee travel and other needs
Companies often prepare an overall budget along with smaller ones for cash flow or operations.
4) Managing and Assessing Risk
Financial Managers find possible money-related risks and prepare plans to handle them. Some risks include:
a) Market Risk: Changes in the economy or industry
b) Credit Risk: Customers not paying on time
c) Liquidity Risk: Not having enough cash for bills
d) Operational Risk: Issues like cyber-attacks or fraud
Effective Risk Management safeguards financial stability and business continuity.
5) Static vs Flexible Budgeting
a) Static Budgeting: A fixed budget that stays the same even if income, expenses, or business conditions change. It’s simple but less adaptable.
b) Flexible Budgeting: A budget that changes based on actual business performance, income, or expenses, making it more accurate and responsive.
Transform your accounting knowledge. Join our Corporate and Business Law (LW) Training today!
How to Start a Career in Financial Management?
To start a career in Financial Management, consider the following steps:
1) Educational Requirements
A bachelor’s degree in finance, business management or a related field is usually the minimum qualification for Financial Management roles. A master’s degree is often beneficial (and sometimes required) for advanced or senior-level positions.
2) Certifications
While certifications are not mandatory, they are valuable for those pursuing a long-term career in Financial Management. Professional bodies offer these credentials and may be tailored for specific career paths.
3) Experience
Gaining professional experience in finance or business management is the key to progressing into senior Financial Management roles. Typically, you’ll need around five years of entry to mid-level experience before qualifying for a management position. Since these roles involve overseeing teams, building strong leadership skills is equally important for career advancement.
Top Careers in Financial Management
If you're aiming for a career in corporate Financial Management, here are some lucrative options for you:
1) Accountant
Accountants maintain financial records, ensure regulatory compliance and offer financial insights to individuals or organisations. Their responsibilities include preparing financial statements, managing taxes, maintaining accurate ledgers and ensuring transparent financial reporting. Many also support management accounting functions such as analysing profitability and departmental spending.
2) Financial Analyst
Financial Analysts assess the financial health of individuals or large organisations. They analyse market trends and recommend investment opportunities based on goals and risk tolerance. Their objective is to position companies for long-term financial stability.
3) Financial Advisor
Personal Financial Advisors help individuals plan and manage their financial futures. They provide assistance with budgeting, investments, retirement planning, education savings, taxes, insurance and estate planning. Advisors may work independently or within investment firms.
4) Financial Manager
Financial Managers develop strategic financial plans that support organisational goals. They prepare financial projections, analyse performance variances, build budgets, improve cash flow, identify investment options and implement cost-saving measures. Their role is critical in sustaining financial health and guiding key financial decisions.
Conclusion
Understanding what is Financial Management is key to building a successful and sustainable business. It helps organisations plan better, control costs, manage risks and make smarter decisions for growth. By using resources wisely and focusing on long-term stability, businesses can improve profitability and stay competitive. Understanding these principles empowers individuals and companies to set a solid foundation for sustained success and future opportunities.
Step into finance leadership. Join our ACCA Applied Skills Training now and master key financial techniques.
 Have Any Question?
Have Any Question?
 +44 7452 122728
+44 7452 122728






 Back
Back







 44 7452 122728
44 7452 122728





