Table Of Contents


Accounting is the core language of any business, and like any language, it has its own rules. These rules, known as Accounting Principles, shape how companies record, present and interpret their finances. They are the foundation of reliable reporting as they ensure accuracy and build trust among shareholders, creditors, and other interested parties.
This blog explores the major Accounting Principles that shape financial reporting from foundational concepts to global standards like GAAP and IFRS. So read on, be fluent in the language of business and become a master at decoding the financial health of any organisation!
What are Accounting Principles?
Accounting Principles are rules that guide how companies record and report their financial activities. They ensure financial statements are consistent and clear, making it harder for businesses to hide details or exaggerate results. This consistency also helps people understand a company’s financial health and compare it with others across different time periods.
These Accounting Principles explain how transactions like sales, purchases, and payments should be reported. Before they existed, companies could present financial data however they wanted, which made comparisons difficult and allowed numbers to be easily distorted. For investors and regulators, this created major problems.
Why are Accounting Principles Important?
Accounting Principles play a vital role in business for several reasons. Here is why they are important:
1) Ensure Accuracy and Reliability: They ensure financial statements are accurate and reliable.
2) Standardise Financial Reporting: They define how expenses, income, assets, liabilities, profits, and losses should be reported.
3) Enable Comparability: They make it easier to compare financial data across companies and time periods.
4) Promote Transparency and Fraud Detection: They promote transparency and help in detecting financial fraud effectively.
5) Support Investor Decision-making: They provide investors with clear information to analyse and make sound financial decisions.
The Different Types of Accounting Principles
There are several basic accounting principles that Investors and Accountants follow to ensure accurate and fair financial processes. Understanding these principles helps businesses maintain transparency and allows users of financial statements to make informed decisions. Below are the key types of Accounting Principles explained clearly.
1) Consistency Principle
The consistency principle is essential for making financial information reliable and easy to compare. It applies to all businesses, whether private or public, and ensures financial statements are prepared in the same way over time. Once a company chooses an accounting method, such as a cash basis or accrual, it should use it consistently across reporting periods.
2) Conservatism Principle
The principle of conservatism helps businesses, especially small ones, manage their finances wisely. It encourages companies to be cautious by recognising expenses and liabilities as soon as they are likely to occur. For small businesses, this approach can prevent risky decision-making and make balance sheets more reliable.
3) Cost Principle
Under the cost principle, assets are recorded at their original purchase price at the time they are acquired. This ensures objectivity and accuracy in financial reporting. Although depreciation may adjust the asset’s value over time, the original cost remains the foundation of its recorded value. This method avoids guesswork and keeps records factual.
4) Economic Entity Principle
The economic entity principle requires that a company’s financial activities be kept separate from those of its owners. This means the company must maintain its own accounting records, bank accounts, and financial statements, independent of personal transactions.

5) Matching Principle
Based on this principle, all expenses pertaining to earning revenue must be recorded at the same time that the revenue is recognised. This prevents the company from overstating its profits by recording income in one period and delaying the related costs to another.
6) Materiality Principle
One of the most crucial Principles of Accounting, the materiality principle requires companies to include all information in their financial statements that could influence the decisions of investors, creditors or other stakeholders. If a piece of financial data is important enough to affect how someone evaluates the company’s performance, it must be disclosed clearly.
7) Full Disclosure Principle
This principle requires companies to share all relevant information in their financial statements. This means that any details that could impact a user’s understanding must be clearly reported. It includes major write-downs or the method used to calculate depreciation.
8) Going Concern Principle
The going concern principle assumes that a business will keep running for the foreseeable future unless there’s clear evidence it won’t. This approach lets companies value their assets and liabilities as if operations will continue. It helps create accurate and realistic financial reports.
9) Monetary Unit Principle
The monetary unit principle states that only transactions measurable in monetary terms should be included in accounting records. Intangible factors like skills, morale, or brand image are excluded. It also assumes a stable currency value, ensuring consistency and reliability in financial reporting over time.
10) Reliability Principle
The reliability principle states that only transactions backed by verifiable evidence should be recorded in the financial statements. This evidence could include receipts, invoices, contracts, bank statements, or other official documents that prove the transaction actually took place.
11) Time Period Principle
This principle in financial reporting ensures that businesses present their performance over consistent time frames. It is about giving a clear and accurate picture of a company’s financial health. This principle helps businesses of all sizes, from small firms to global corporations, produce reliable financial statements. These can be compared across different periods.
12) Revenue Recognition Principle
This principle states that revenue must be recorded only when it has been both earned and can be reasonably measured. In other words, a company must recognise revenue when it has delivered goods or services, and payment is either received or assured.

13) Accrual Principle
The accrual principle in accounting records the expenses and income when they are earned or incurred, not when cash changes hands. This ensures that a company’s financial performance is shown accurately in its financial statements at any given time.
14) Objectivity Principle
This is one of the most important principles of accounting. It states that all financial information must be based on unbiased evidence and not influenced by personal opinions. It highlights the importance of using verifiable documents such as invoices, receipts, contracts, and bank statements to support accounting records.
Role of Accounting Principles
Accounting Principles play a vital role in ensuring that financial information is recorded in a clear, consistent, and reliable manner. These principles also help prevent errors, manipulation, and misrepresentation of financial data by promoting transparency and ethical reporting. Key roles of Accounting Principles include:
1) Ensure consistency in financial reporting across different accounting periods
2) Improve the accuracy and reliability of financial records
3) Support informed decision-making for investors and management
4) Promote transparency and ethical business practices
5) Help maintain compliance with legal and regulatory standards
6) Enable easy comparison between different organisations
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
In the UK, companies follow a set of rules called Generally Accepted Accounting Principles in the United Kingdom (UK GAAP) to keep financial reporting clear and consistent. These rules are created by the Financial Reporting Council (FRC). Although there isn’t one fixed list, these principles form the basis of UK GAAP: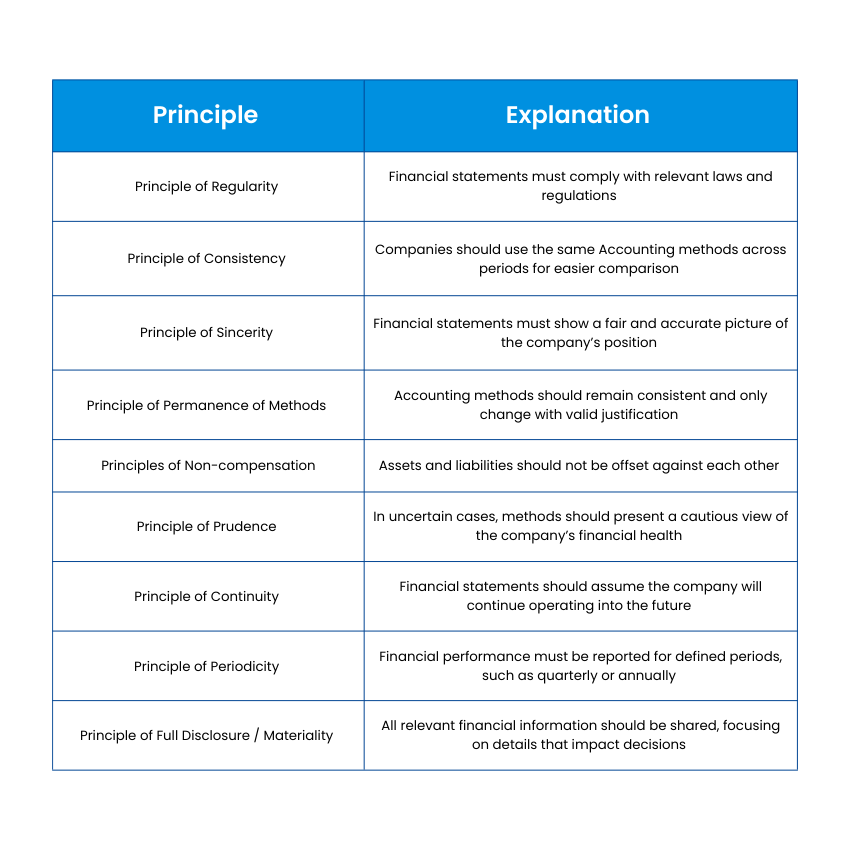
Advantages of Accounting Principles
By following the Accounting Principles, companies can maintain transparency, build trust with stakeholders, and reduce the risk of financial misstatements or fraudulent reporting. The following are the major advantages of implementing those principles:
1) Financial Clarity: Presents business performance in a structured and easily understandable way.
2) Business Credibility: Builds trust with investors, banks, and stakeholders through standardised reporting.
3) Risk Control: Reduces the chances of errors, fraud, and financial manipulation.
4) Strategic Planning: Helps management plan budgets, investments, and future growth with reliable data.
5) Audit Readiness: Makes audits smoother by maintaining systematic and verifiable records.
6) Long-term Stability: Supports sustainable business operations through consistent financial practices.
Disadvantages of Accounting Principles
While Accounting Principles are essential for bookkeeping, they do have certain drawbacks. These can affect how a company’s finances are shown. Some key limitations include:
1) Records are only measured in monetary terms. Events that impact a business but cannot be expressed in money are not included.
2) These principles follow the “time value of money” and record assets at historical cost. They ignore current market changes, which may not reflect the true financial position.
3) Only past transactions are recorded. Standards like GAAP do not account for future events that could influence finances.
4) More focus is placed on forms and tables rather than explaining important details. This can reduce the depth of financial information.
Conclusion
In the field of Finance, Accounting Principles are the foundation of transparency, trust and consistency. By understanding their types and global frameworks like GAAP and IFRS, businesses and investors gain greater clarity. Whether for local or international businesses, these principles ensure financial information speaks the same language.
 Have Any Question?
Have Any Question?
 +44 7452 122728
+44 7452 122728






 Back
Back







 44 7452 122728
44 7452 122728




