Table Of Contents


Imagine running a business with financial records that are always clear, accurate, and balanced. This is not possible merely through careful tracking. It is due to Double-entry Bookkeeping, a system that records every transaction in two accounts to keep financial information reliable and organised.
Understanding What is Double-entry Bookkeeping helps businesses maintain accuracy, prevent costly mistakes, and ensure financial stability. In this blog, we will discuss what it is, its fundamental rules, how it benefits businesses of all sizes and much more.
What is Double-entry Bookkeeping?
Double-entry Bookkeeping is a system used to record financial transactions. Every transaction affects at least two accounts—one account is debited, and another is credited. This method ensures that the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) stays balanced. Businesses use this system to keep their financial records accurate and organised.
In this system, every financial activity has two sides. For example, if a company buys office furniture for cash, the Furniture (Asset) account increases, while the Cash (Asset) account decreases. This approach helps businesses track where money is coming from and where it is going. It also makes it easier to find mistakes since the totals must always match.
Who Uses the Double-entry Bookkeeping?
The double-entry system is widely utilised across the world. Here is a list of bodies that use this accounting system
Businesses in the United Kingdom (UK)
1) UK companies follow accounting standards set by the Financial Reporting Council (FRC).
2) Most organisations prepare accounts using UK Generally Accepted Accounting Practice (UK GAAP) or IFRS.
3) Both UK GAAP and IFRS require the use of the Double-entry Bookkeeping system for accuracy and transparency.
4) Limited companies in the UK must maintain double-entry records to produce statutory financial statements.
Businesses in the United States (US)
1) The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) sets official accounting rules.
2) These rules are known as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
3) GAAP requires companies to use the double-entry system for financial reporting.
Businesses Outside the UK and US
1) International companies follow standards defined by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB).
2) These standards are called International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
3) IFRS also requires organisations to use the double-entry system to maintain consistency.
Public Companies (Worldwide)
1) They must maintain a Double-entry Bookkeeping system.
2) Public companies in the UK follow UK GAAP or IFRS, while others use GAAP or IFRS based on jurisdiction.
Small Businesses
1) In the UK, small businesses often adopt Double-entry Bookkeeping when their transactions become more complex or when preparing for growth, loans or investment.
2) Using double-entry records improves accuracy and provides a clear overview of financial performance.

Fundamental Rules of Double-entry Bookkeeping
Here are the basic rules of Double-entry Bookkeeping:
1) Every Transaction has Two Sides: One account is debited, and another is credited.
2) Debits Must Equal Credits: The total amount of debits must always match the total credits.
3) Assets Increase with Debits: When a business gets cash or property, it is recorded as a debit.
4) Liabilities Increase with Credits: When a business borrows money or owes something, it is recorded as a credit.
5) Equity is Affected by Profits and Losses: Profits increase equity, while losses decrease it.
Learn to interpret business trends and make smarter operational choices with Management Information (MI) Training today!
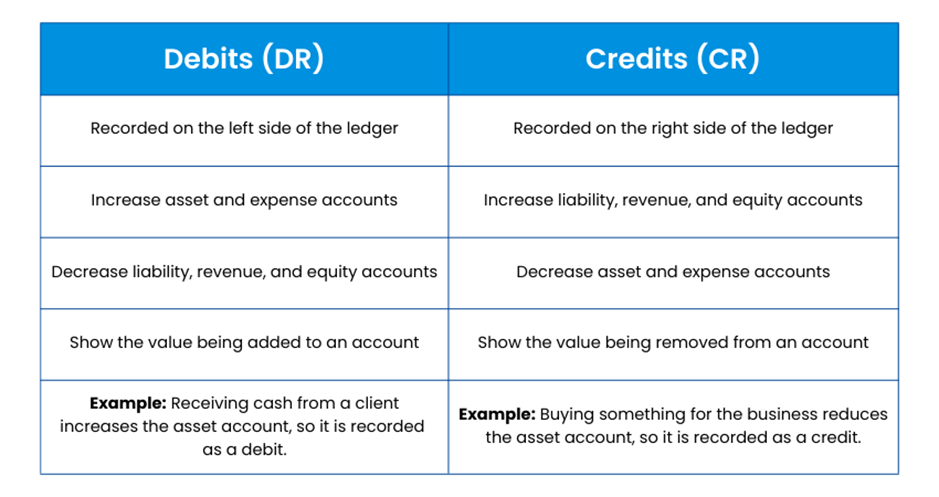
What are Debits and Credits?
In Double-entry Bookkeeping, debits and credits represent two sides of a financial transaction. They work together to keep accounts in balance. Let’s look at the two sides of a financial transaction.
Debits
Debits record the value entering a business. They typically reflect growth in assets or operating costs. When a company receives cash, buys equipment, or pays an expense, the debit entry shows where the value is being added.
Credits
Credits record the value leaving a business or obligations owed. They usually show increases in income, liabilities, or equity. When a company earns revenue, takes a loan, or reduces an asset, the credit entry indicates where the value is being taken from. This is a core concept featured in Credit Control Interview Questions for understanding how organisations assess and manage payments due.
The Accounting Equation
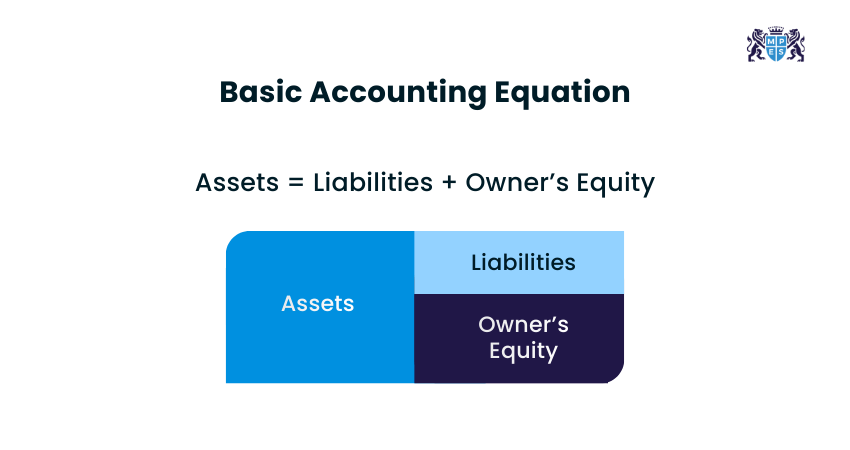
The accounting equation is valuable since it helps to maintain accuracy in Double-entry Bookkeeping. It has a simple equation:
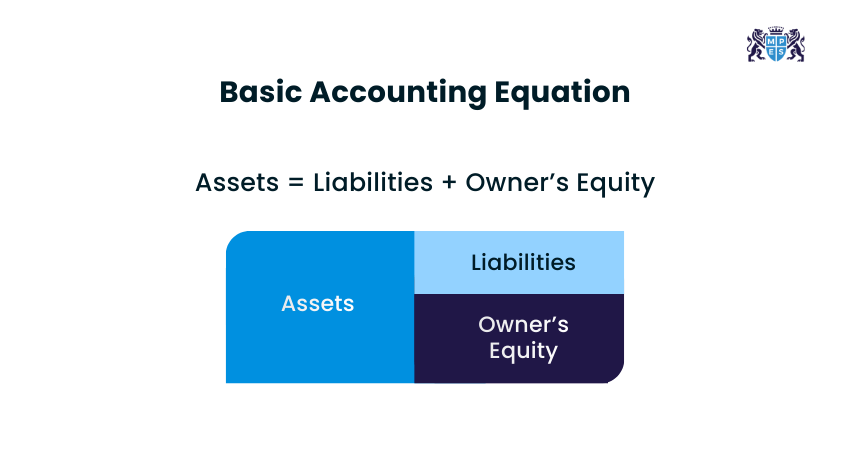
This equation depicts that whenever there is an asset change, there must be an equal change in liabilities or equity.
For example, an e-commerce company purchases £1,000 of inventory on credit. Here, assets increase because inventory rises and liabilities also increase since accounts payable rise.
Different Types of Accounts in Double-entry Bookkeeping
Here are the account types in Double-entry Bookkeeping:
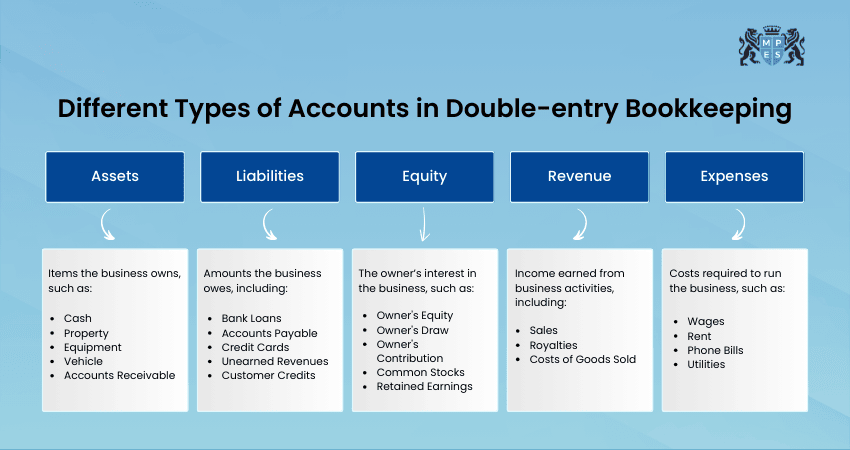
Asset Accounts
This account records what a business owns, such as cash, property, and equipment. These accounts increase when the business receives something valuable. They decrease when assets are used or spent.
Examples:
1) Cash in the bank
2) Business vehicles
3) Office equipment
Liability Accounts
This account tracks what a business owes to others, like loans and unpaid bills. They increase when a business borrows money and decrease when debts are paid. Keeping track of liabilities helps businesses manage their financial responsibilities.
Examples:
1) Bank loan
2) Unpaid supplier invoices
3) Credit card debt
Equity Accounts
This account shows the owner’s share in the business after all debts are paid. When a business earns a profit, equity increases, and when it has losses, equity decreases. Equity also grows when the owner invests more money into the business.
Examples:
1) Owner’s capital
2) Retained earnings (profits kept in the business)
3) Owner withdrawals (money taken out by the owner)
Income Accounts
This account records the money a business earns from selling products or services. These accounts increase when a business makes a sale and help measure profitability. Recording income properly helps businesses understand their financial growth.
Examples:
1) Sales revenue
2) Service fees
3) Rental income
Expense Accounts
This account records the money a business spends to run operations, like rent, salaries, and supplies. These accounts increase when the business spends money and decrease when expenses are reduced. Managing expenses is important for maintaining profits.
Examples:
1) Rent payments
2) Employee salaries
3) Office supplies
Strengthen your tax knowledge with the Principles of Taxation (PTX) Course - Register today!
Advantages of Double-entry Bookkeeping
Here are the benefits of Double-entry Bookkeeping:

1) Ensures Accuracy
1) Every transaction is recorded twice, reducing mistakes
2) Keeps financial records balanced and organised
3) Helps businesses track their real profits and losses
2) Helps Prevent Errors
1) Mistakes are easier to find since each entry has a matching record
2) Reduces the risk of missing or incorrect transactions
3) Ensures that all money coming in and going out is properly recorded
3) Creates a Clear Audit Trail
1) Keeps a detailed history of all financial transactions
2) Helps businesses prepare for tax audits or financial checks
3) Makes it easier to track changes in business finances over time
4) Simplifies Financial Statement Preparation
1) Organised records make it easier to create balance sheets and income statements
2) Helps businesses understand their financial position quickly
3) Makes tax filing and financial reporting less complicated
5) Helps Organisations Make Better Financial Decisions
1) Accurate statements reveal profit levels and how each business part is doing
2) Reliable records show where money comes from and where it goes
3) Helps to plan resources, manage debt, and evaluate new investments
Single-entry vs Double-entry Accounting
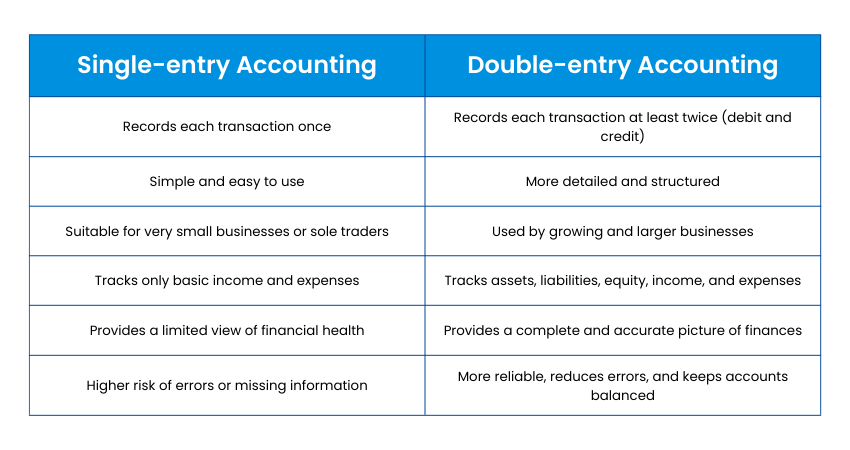
Single-entry Accounting records each transaction only once. It is simple to maintain and is used by small businesses or sole traders. Because it captures limited details, it offers only a basic view of income and expenses and carries a higher risk of missing information.
On the other hand, Double-entry Accounting records transactions twice, once when debited and again when credited. This gives the complete picture of a business’s financial position. It is useful for tracking assets, liabilities, income and expenses. It is preferred by large-sized businesses.
Practical Examples of Double-entry Bookkeeping
Here are some examples to show how businesses record financial transactions accurately:
1) Purchasing Goods on Credit
1) When a business buys goods but pays later, it records the purchase as an expense
2) The same amount is also recorded as a liability since the business owes money
3) Once the payment is made, the liability decreases, and cash is deducted
2) Receiving a Business Loan
1) A business receives money from a loan, increasing its cash balance
2) At the same time, it records the loan as a liability since it must be repaid
3) As payments are made, the liability decreases, and cash is deducted
3) Paying Business Expenses
1) When a business pays rent or salaries, it records the amount as an expense
2) The same amount is deducted from the cash account
3) This shows the business used cash to cover its running costs
4) Contributing Capital to the Business
1) When an owner invests money into the business, it increases the capital account
2) The same amount is added to the business’s cash or bank account
3) This records the owner’s contribution and strengthens the business’s financial position
Conclusion
Understanding What is Double-entry Bookkeeping helps businesses to maintain accurate and reliable financial records. This system records transactions twice, improving reliability and minimising errors. Organisations of all sizes utilise it for monitoring income and financial health. By using Double-entry Bookkeeping, businesses can effectively manage finances and make informed decisions.
Build strong audit knowledge with Assurance (AS) Training today!
 Have Any Question?
Have Any Question?
 +44 7452 122728
+44 7452 122728






 Back
Back







 44 7452 122728
44 7452 122728





